-
Table of Contents
What are the Interactions of Ibuprofen with Other Drugs?
Ibuprofen is a widely used nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that helps alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and lower fever. While it is generally considered safe for short-term use, it is crucial to understand its interactions with other medications. These interactions can lead to adverse effects or diminish the effectiveness of treatments. This article explores the various drug interactions associated with ibuprofen, providing valuable insights for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Understanding Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, chemicals in the body that promote inflammation, pain, and fever. It is commonly used to treat conditions such as:
- Headaches
- Muscle aches
- Arthritis
- Menstrual cramps
- Dental pain
Despite its effectiveness, ibuprofen can interact with various medications, leading to potential health risks. Understanding these interactions is essential for safe medication management.
Common Drug Interactions with Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen can interact with several classes of medications, which may enhance side effects or reduce therapeutic efficacy. Here are some notable interactions:
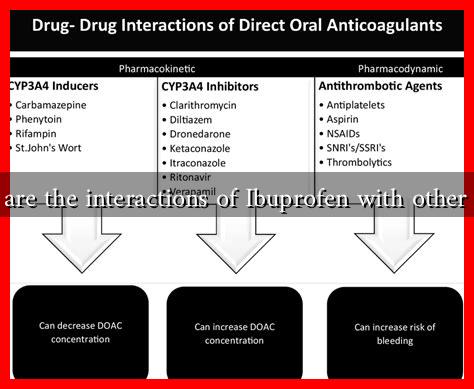
1. Anticoagulants
Ibuprofen can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with anticoagulants such as:
- Warfarin
- Heparin
- Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs)
Studies have shown that the combination of ibuprofen and warfarin can lead to a significant increase in the International Normalized Ratio (INR), which measures blood coagulation. This can result in a higher risk of hemorrhage.
2. Other NSAIDs
Taking ibuprofen with other NSAIDs, such as naproxen or aspirin, can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers. The combined anti-inflammatory effects can also lead to renal impairment.
3. Antihypertensives
Ibuprofen may reduce the effectiveness of certain antihypertensive medications, including:
- ACE inhibitors (e.g., lisinopril)
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Diuretics
Research indicates that NSAIDs can lead to sodium retention and increased blood pressure, counteracting the effects of these medications.
4. Corticosteroids
When ibuprofen is taken alongside corticosteroids, such as prednisone, the risk of gastrointestinal side effects, including ulcers and bleeding, is heightened. This combination should be approached with caution.
Case Studies and Statistics
A study published in the *British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology* found that patients taking ibuprofen alongside anticoagulants had a 50% higher risk of major bleeding events compared to those not on ibuprofen. Another research article in *The Journal of Hypertension* highlighted that patients using NSAIDs experienced a 30% increase in blood pressure compared to those who did not.
Recommendations for Safe Use
To minimize the risk of drug interactions with ibuprofen, consider the following recommendations:
- Always inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Avoid combining ibuprofen with other NSAIDs unless directed by a healthcare professional.
- Monitor blood pressure regularly if you are on antihypertensive medications and using ibuprofen.
- Consult your doctor before starting ibuprofen if you are on anticoagulants or corticosteroids.
Conclusion
Ibuprofen is an effective medication for managing pain and inflammation, but its interactions with other drugs can pose significant risks. Understanding these interactions is crucial for safe medication use. Patients should always communicate openly with their healthcare providers about their medication regimens to avoid adverse effects. By being informed and cautious, individuals can safely benefit from ibuprofen while minimizing potential risks.
For more information on drug interactions and safe medication practices, visit the Drugs.com Drug Interactions Checker.