-
Table of Contents
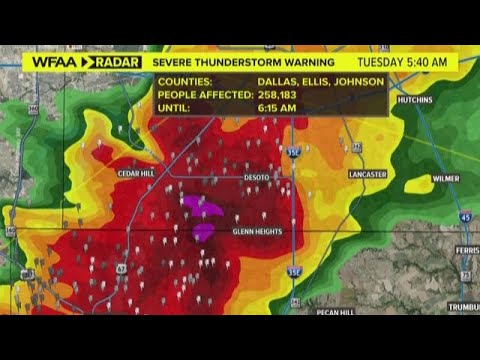
Thunderstorm Warning Issued Across Regions
As the summer months approach, the frequency and intensity of thunderstorms increase, prompting meteorological agencies to issue warnings across various regions. Thunderstorms can bring heavy rainfall, strong winds, hail, and even tornadoes, posing significant risks to life and property. This article delves into the implications of thunderstorm warnings, the science behind these weather phenomena, and the necessary precautions individuals and communities should take.
The Science Behind Thunderstorms
Thunderstorms are a result of atmospheric instability, where warm, moist air rises and cools, leading to condensation and the formation of clouds. The key ingredients for a thunderstorm include:
- Moisture: Essential for cloud formation and precipitation.
- Instability: Warm air must rise rapidly to create strong updrafts.
- Lift: Mechanisms such as fronts, sea breezes, or mountains that force air upward.
When these elements come together, they can produce severe thunderstorms capable of generating lightning, heavy rain, and damaging winds. According to the National Weather Service (NWS), approximately 10% of thunderstorms become severe, leading to significant weather-related incidents.
Understanding Thunderstorm Warnings
Thunderstorm warnings are issued to alert the public about impending severe weather conditions.
. There are different types of warnings, including:
- Severe Thunderstorm Watch: Conditions are favorable for severe thunderstorms to develop.
- Severe Thunderstorm Warning: A severe thunderstorm has been detected by radar or reported by spotters.
- Flash Flood Warning: Flash flooding is imminent or occurring due to heavy rainfall.
These warnings are crucial for public safety, allowing individuals to take necessary precautions. For instance, during a severe thunderstorm warning, people are advised to seek shelter indoors, avoid using electrical appliances, and stay away from windows.
Recent Thunderstorm Events and Their Impact
In recent years, several regions have experienced devastating thunderstorms that resulted in significant damage and loss of life. For example:
- Midwest Tornado Outbreak (2021): A series of thunderstorms produced multiple tornadoes across the Midwest, causing extensive damage to homes and infrastructure.
- Florida Thunderstorm (2022): A severe thunderstorm led to flash flooding in parts of Florida, prompting emergency evacuations and road closures.
- Texas Storms (2023): Severe thunderstorms brought hail the size of golf balls, damaging crops and vehicles.
These events highlight the importance of timely warnings and preparedness. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), over 1,000 people are injured each year due to thunderstorms, underscoring the need for public awareness and education.
Preparedness and Safety Measures
Being prepared for thunderstorms can significantly reduce risks. Here are some essential safety measures:
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather updates through local news, weather apps, or the NWS website.
- Create an Emergency Kit: Include essentials such as water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, and a first-aid kit.
- Have a Plan: Establish a family communication plan and identify safe locations to take shelter.
- Secure Outdoor Items: Bring in or secure any loose items that could become projectiles in strong winds.
For more detailed information on thunderstorm preparedness, visit the [Ready.gov website](https://www.ready.gov/thunderstorms-lightning).
Conclusion
Thunderstorm warnings serve as a critical tool for public safety, providing essential information that can save lives and minimize property damage. Understanding the science behind thunderstorms, recognizing the different types of warnings, and implementing safety measures are vital steps in preparing for severe weather. As climate change continues to influence weather patterns, the frequency and intensity of thunderstorms may increase, making it imperative for communities to stay informed and prepared. By taking proactive measures, individuals can protect themselves and their loved ones from the dangers posed by thunderstorms.