-
Table of Contents
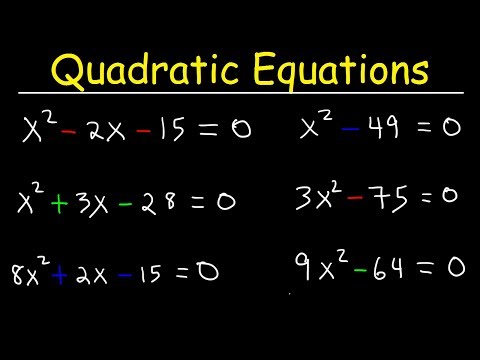
Quadratic Equation Problems with Solutions
Quadratic equations are a fundamental concept in algebra that involve a variable raised to the second power. They are commonly used in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics to model real-world situations. Understanding how to solve quadratic equation problems is essential for students and professionals alike. In this article, we will explore some common quadratic equation problems and provide step-by-step solutions.
Problem 1: Finding the Roots of a Quadratic Equation
One of the most basic problems involving quadratic equations is finding the roots, or solutions, of the equation. The general form of a quadratic equation is ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants.
. To find the roots of the equation, we can use the quadratic formula:
x = (-b ± √(b2 – 4ac)) / 2a
Let’s consider an example:
Find the roots of the equation x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
Using the quadratic formula, we have:
- a = 1, b = -5, c = 6
- Substitute the values into the formula:
x = (5 ± √(25 – 24)) / 2
x = (5 ± 1) / 2
Therefore, the roots of the equation are x = 3 and x = 2.
Problem 2: Applications of Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations are not just theoretical concepts; they have practical applications in various fields. One common application is in projectile motion problems. When an object is thrown into the air, its height can be modeled by a quadratic equation. Let’s consider an example:
An object is thrown into the air with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. The height of the object at any time t can be modeled by the equation h(t) = -4.9t2 + 20t, where t is the time in seconds. Find the maximum height reached by the object.
To find the maximum height, we need to determine the vertex of the parabola represented by the quadratic equation. The vertex can be found using the formula t = –b / 2a. In this case, a = -4.9 and b = 20.
Substitute the values into the formula:
t = -20 / (2 * -4.9) = 2.04 seconds
Substitute t = 2.04 back into the equation to find the maximum height:
h(2.04) = -4.9(2.04)2 + 20(2.04) = 20.4 meters
Therefore, the maximum height reached by the object is 20.4 meters.
Conclusion
Quadratic equations are powerful tools that can be used to solve a wide range of problems in various fields. By understanding how to solve quadratic equation problems, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and tackle complex real-world scenarios with confidence. Remember to practice solving different types of quadratic equation problems to strengthen your understanding of the concepts.
For more information on quadratic equations and their applications, you can visit Math is Fun.