-
Table of Contents
NOROVIRUS: HOW DOES IT SPREAD
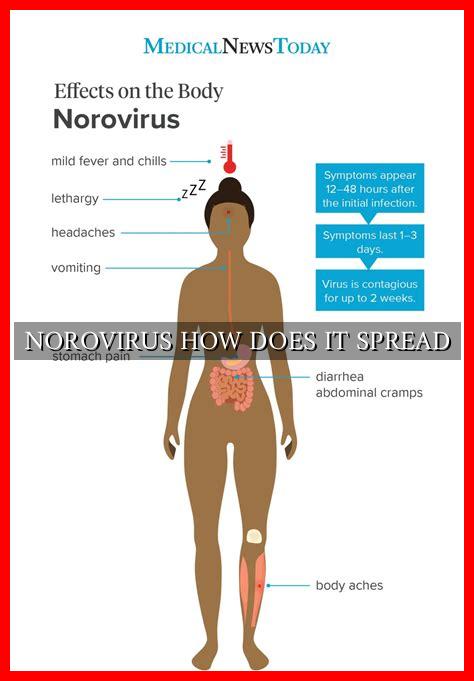
Norovirus is a highly contagious virus that causes gastroenteritis, commonly known as the stomach flu. It is responsible for a significant number of outbreaks of foodborne illness each year, affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding how norovirus spreads is crucial in preventing its transmission and controlling outbreaks.
What is Norovirus?
Norovirus is a group of viruses that cause inflammation of the stomach and intestines. It is the leading cause of gastroenteritis in the United States, with symptoms including diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, and stomach cramps. The virus is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person.
How Does Norovirus Spread?
Norovirus spreads through various routes, primarily through:
- Person-to-Person Contact: Direct contact with an infected person, such as caring for someone who is sick or sharing food or utensils with them, can lead to the transmission of norovirus.
- Contaminated Surfaces: Norovirus can survive on surfaces for days, making it easy to spread through touching contaminated objects and then touching your mouth, nose, or eyes.
- Contaminated Food and Water: Consuming food or water that has been contaminated with norovirus is a common way the virus spreads, especially in settings like restaurants, cruise ships, and schools.
High-Risk Settings for Norovirus Outbreaks
Some environments are more prone to norovirus outbreaks due to close contact and shared facilities.
. These include:
- Cruise Ships: The close quarters and shared dining areas on cruise ships make them a breeding ground for norovirus outbreaks.
- Long-Term Care Facilities: Nursing homes and assisted living facilities are at high risk due to the vulnerable population and communal living arrangements.
- Schools and Daycares: Children are more susceptible to norovirus, and the close contact in school settings can lead to rapid spread.
Preventing Norovirus Spread
There are several measures that can be taken to prevent the spread of norovirus:
- Hand Hygiene: Washing hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds is one of the most effective ways to prevent norovirus transmission.
- Disinfection: Cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces regularly can help prevent the spread of norovirus.
- Food Safety: Proper food handling and preparation practices can reduce the risk of norovirus contamination in food.
Conclusion
Norovirus is a highly contagious virus that spreads easily through person-to-person contact, contaminated surfaces, and food and water. Understanding how norovirus spreads and taking preventive measures such as hand hygiene, disinfection, and food safety practices can help control outbreaks and protect against infection. By being aware of the risk factors and implementing proper precautions, we can reduce the incidence of norovirus infections and safeguard public health.
For more information on norovirus and its prevention, visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website.