-
Table of Contents
MULTIPLE INHERITANCE IN JAVA
Multiple inheritance is a concept in object-oriented programming where a class can inherit attributes and methods from more than one parent class. While Java does not support multiple inheritance of classes, it does allow for multiple inheritance of interfaces. In this article, we will explore the concept of multiple inheritance in Java, its advantages, disadvantages, and how it can be achieved using interfaces.
Understanding Inheritance in Java
Inheritance is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming that allows a class to inherit attributes and methods from another class. In Java, a class can only inherit from one superclass, which is known as single inheritance. This means that a class can have only one direct parent class.
Advantages of Multiple Inheritance
- Code Reusability: Multiple inheritance allows for the reuse of code from multiple parent classes, reducing redundancy and improving maintainability.
- Flexibility: It provides flexibility in designing classes by allowing them to inherit behavior from different sources.
- Modularity: Multiple inheritance can help in breaking down complex systems into smaller, more manageable components.
Disadvantages of Multiple Inheritance
- Diamond Problem: One of the main challenges of multiple inheritance is the diamond problem, where a class inherits from two classes that have a common ancestor.
. This can lead to ambiguity in method resolution.
- Complexity: Multiple inheritance can make the codebase more complex and harder to understand, especially when dealing with a large number of parent classes.
- Namespace Pollution: It can lead to namespace conflicts when two parent classes have methods or attributes with the same name.
Implementing Multiple Inheritance in Java
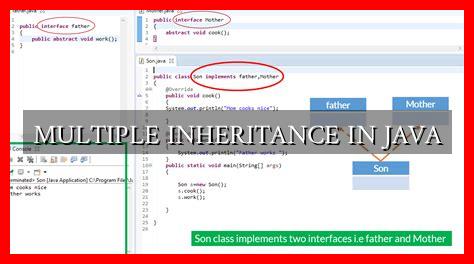
While Java does not support multiple inheritance of classes, it does allow for multiple inheritance of interfaces. Interfaces in Java are similar to abstract classes but can only contain method signatures and constants. By implementing multiple interfaces, a class can inherit behavior from multiple sources.
Here is an example of how multiple inheritance can be achieved using interfaces in Java:
“`java
interface A {
void methodA();
}
interface B {
void methodB();
}
class MyClass implements A, B {
public void methodA() {
System.out.println(“Method A”);
}
public void methodB() {
System.out.println(“Method B”);
}
}
“`
In the above example, the class `MyClass` implements both interfaces `A` and `B`, allowing it to inherit behavior from both interfaces.
Conclusion
While Java does not support multiple inheritance of classes, it does provide a way to achieve multiple inheritance through interfaces. By implementing multiple interfaces, a class can inherit behavior from multiple sources, providing code reusability and flexibility in design. However, developers should be aware of the potential challenges such as the diamond problem and namespace pollution when using multiple inheritance in Java.
Overall, understanding the concept of multiple inheritance in Java and how it can be implemented using interfaces is essential for building robust and maintainable software systems.