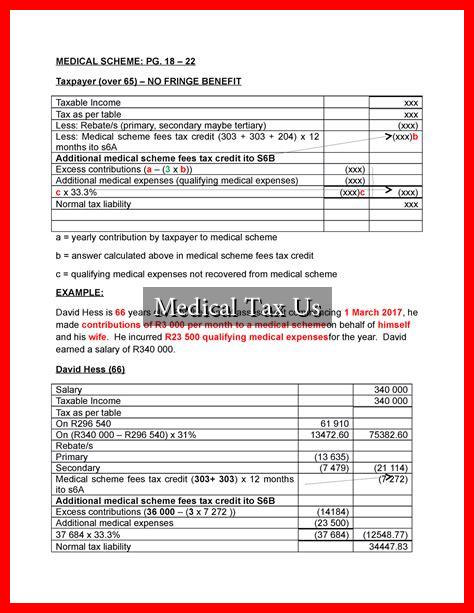
-
Table of Contents
Understanding Medical Tax Us: A Comprehensive Guide
In the United States, the intersection of healthcare and taxation is a complex landscape that affects millions of individuals and families. Medical tax, often referred to as medical expense deductions, plays a crucial role in how taxpayers manage their healthcare costs. This article delves into the intricacies of medical tax in the U.S., exploring its implications, benefits, and the nuances that taxpayers should be aware of.
What is Medical Tax?
Medical tax refers to the deductions that taxpayers can claim for qualifying medical expenses on their federal income tax returns. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows taxpayers to deduct certain unreimbursed medical expenses that exceed a specific percentage of their adjusted gross income (AGI). This deduction can significantly alleviate the financial burden of healthcare costs for many families.
Eligibility for Medical Expense Deductions
To qualify for medical expense deductions, taxpayers must meet specific criteria set by the IRS.
. Here are the key points to consider:
- Threshold Requirement: As of the 2023 tax year, taxpayers can deduct unreimbursed medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of their AGI.
- Qualified Expenses: Eligible expenses include payments for medical care, dental care, vision care, and certain long-term care services.
- Itemization Required: Taxpayers must itemize their deductions on Schedule A of Form 1040 to claim medical expenses.
Common Qualifying Medical Expenses
Understanding what qualifies as a medical expense is crucial for maximizing deductions. Some common qualifying expenses include:
- Doctor and hospital visits
- Prescription medications
- Medical equipment (e.g., wheelchairs, crutches)
- Dental treatments (e.g., braces, fillings)
- Vision care (e.g., glasses, contact lenses)
- Health insurance premiums
Case Study: The Impact of Medical Tax Deductions
Consider the case of the Johnson family, who incurred significant medical expenses due to a family member’s chronic illness. In 2022, their AGI was $80,000, and they had $15,000 in qualifying medical expenses. Here’s how the deduction worked for them:
- 7.5% of AGI: $80,000 x 0.075 = $6,000
- Eligible deduction: $15,000 (total expenses) – $6,000 (threshold) = $9,000
By itemizing their deductions, the Johnsons were able to reduce their taxable income by $9,000, resulting in significant tax savings. This example illustrates how medical tax deductions can provide financial relief for families facing high medical costs.
Challenges and Considerations
While medical tax deductions can be beneficial, there are challenges and considerations that taxpayers should keep in mind:
- Record Keeping: Taxpayers must maintain accurate records of all medical expenses, including receipts and invoices.
- Changes in Tax Law: Tax laws can change, impacting eligibility and deduction limits. Staying informed is essential.
- Alternative Options: Some taxpayers may benefit more from Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) instead of relying solely on medical tax deductions.
Conclusion
Medical tax deductions can provide significant financial relief for taxpayers facing high healthcare costs. Understanding the eligibility criteria, qualifying expenses, and the potential impact on tax liability is crucial for maximizing these benefits. As healthcare costs continue to rise, being informed about medical tax options can empower individuals and families to make better financial decisions. For more detailed information on medical tax deductions, visit the IRS website.
In summary, navigating the complexities of medical tax in the U.S. requires careful planning and awareness of current tax laws. By leveraging available deductions, taxpayers can alleviate some of the financial burdens associated with healthcare, ultimately leading to improved financial well-being.