-
Table of Contents
Lightning: How Does It Form?
Lightning is a fascinating natural phenomenon that has captivated humans for centuries. The sight of a lightning bolt streaking across the sky can be both awe-inspiring and terrifying. But have you ever wondered how lightning actually forms? In this article, we will explore the science behind lightning and uncover the mysteries of this powerful force of nature.
What is Lightning?
Lightning is a sudden electrostatic discharge that occurs during a thunderstorm. It is typically accompanied by thunder, which is the sound produced by the rapid expansion of air heated by the lightning bolt. Lightning can take on various forms, including cloud-to-ground, cloud-to-cloud, and intra-cloud lightning.
How Does Lightning Form?
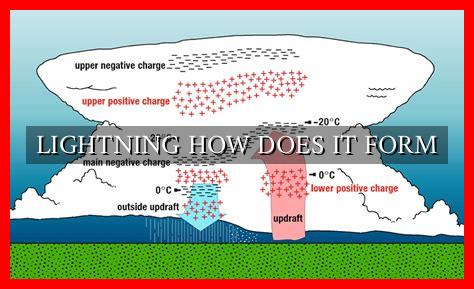
Lightning forms as a result of the buildup of electrical charges within a thunderstorm cloud.
. This process involves several key steps:
- 1. Charge Separation: As a thunderstorm cloud develops, strong updrafts and downdrafts cause ice particles and water droplets to collide. This collision leads to the separation of positive and negative charges within the cloud.
- 2. Formation of Leaders: Once the charge separation reaches a critical point, a stepped leader—a channel of ionized air—begins to form and extend towards the ground.
- 3. Return Stroke: When the stepped leader connects with a positively charged object on the ground, such as a tree or a building, a return stroke occurs. This is the bright flash of lightning that we see.
Types of Lightning
There are several types of lightning, each with its own unique characteristics:
- 1. Cloud-to-Ground Lightning: This is the most common type of lightning and occurs when a stepped leader connects with an object on the ground.
- 2. Cloud-to-Cloud Lightning: This type of lightning occurs between two different cloud systems and is often seen as a flash of light within a cloud.
- 3. Intra-Cloud Lightning: Also known as sheet lightning, this type of lightning occurs within the same cloud and is often seen as a diffuse glow.
Interesting Facts About Lightning
Here are some fascinating facts about lightning:
- 1. The average lightning bolt is about 5 miles long.
- 2. Lightning can reach temperatures of up to 30,000 degrees Celsius—hotter than the surface of the sun.
- 3. The United States experiences over 20 million lightning strikes each year.
Conclusion
Lightning is a powerful and awe-inspiring force of nature that has intrigued humans for centuries. By understanding the science behind how lightning forms, we can better appreciate the beauty and complexity of this natural phenomenon. The next time you witness a lightning storm, remember the intricate process that leads to the creation of those dazzling bolts of light in the sky.
For more information on lightning and thunderstorms, visit the National Weather Service’s Lightning Safety page.