-
Table of Contents
Is Diclofenac Recommended for Chronic Pain Management?
Chronic pain is a complex and often debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Managing this type of pain can be challenging, and various treatment options are available. One medication that has been widely used for pain relief is diclofenac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). This article explores the efficacy, safety, and recommendations surrounding the use of diclofenac for chronic pain management.
Understanding Diclofenac
Diclofenac is a potent NSAID that works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, chemicals in the body that promote inflammation, pain, and fever. It is commonly prescribed for conditions such as arthritis, muscle pain, and other inflammatory disorders. Diclofenac is available in various forms, including oral tablets, topical gels, and injections.
Efficacy of Diclofenac in Chronic Pain Management
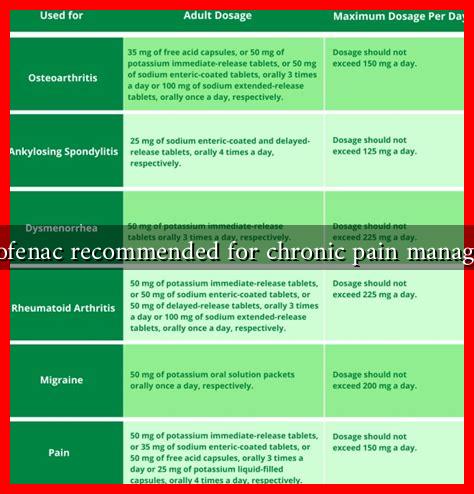
Numerous studies have evaluated the effectiveness of diclofenac in managing chronic pain. Research indicates that diclofenac can provide significant pain relief for various conditions, including:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Chronic back pain
- Musculoskeletal disorders
A meta-analysis published in the journal Pain Physician found that diclofenac was more effective than placebo in reducing pain and improving function in patients with osteoarthritis. Additionally, a study in the British Journal of Sports Medicine demonstrated that topical diclofenac gel provided significant pain relief for patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Safety and Side Effects
While diclofenac can be effective for chronic pain management, it is essential to consider its safety profile. Common side effects include:
- Gastrointestinal issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Skin reactions (rashes, itching)
More serious side effects can occur, particularly with long-term use, such as:
- Cardiovascular risks (increased risk of heart attack and stroke)
- Kidney damage
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
Due to these potential risks, the FDA has issued warnings regarding the long-term use of diclofenac, particularly in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular or gastrointestinal conditions.
Guidelines and Recommendations
Medical guidelines regarding the use of diclofenac for chronic pain management vary. The American College of Rheumatology recommends NSAIDs, including diclofenac, as a first-line treatment for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. However, they emphasize the importance of using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary to minimize risks.
Patients should consult their healthcare providers to determine if diclofenac is appropriate for their specific condition. Factors to consider include:
- Type and severity of pain
- Patient’s medical history
- Potential drug interactions
Alternatives to Diclofenac
For patients who may be at risk for the side effects associated with diclofenac, alternative treatments for chronic pain management include:
- Acetaminophen
- Other NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen)
- Topical analgesics (e.g., capsaicin cream)
- Physical therapy
- Complementary therapies (e.g., acupuncture, yoga)
Conclusion
Diclofenac can be an effective option for managing chronic pain, particularly in conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. However, its use comes with potential risks that must be carefully weighed against the benefits. Patients should engage in open discussions with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate pain management strategy tailored to their individual needs. Ultimately, while diclofenac may be recommended for some, it is crucial to consider alternative therapies and lifestyle modifications to achieve optimal pain relief and improve quality of life.