-
Table of Contents
How to Understand the Impact of Medication on Sexual Function
Sexual function is a complex interplay of physical, psychological, and emotional factors. While many people focus on the benefits of medications for treating various health conditions, the potential side effects on sexual function are often overlooked. Understanding how medications can impact sexual health is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. This article explores the relationship between medication and sexual function, highlighting key factors, examples, and strategies for managing these effects.
The Connection Between Medication and Sexual Function
Medications can influence sexual function in several ways, including:
- Hormonal Changes: Some medications can alter hormone levels, affecting libido and sexual performance.
- Blood Flow: Certain drugs may impact blood circulation, which is essential for sexual arousal and function.
- Neurological Effects: Medications that affect the nervous system can lead to changes in sexual desire and response.
- Psychological Impact: The side effects of medications can lead to anxiety or depression, further complicating sexual function.
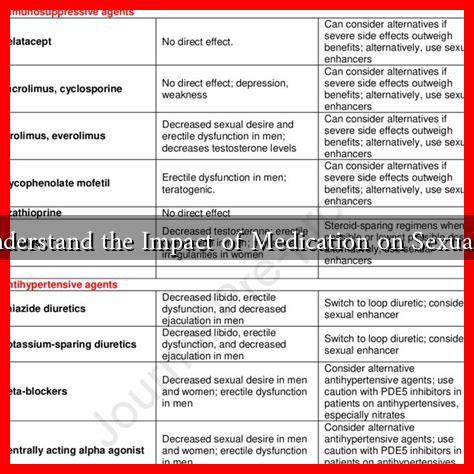
Common Medications That Affect Sexual Function
Several classes of medications are known to have side effects that can impact sexual health. Here are some common examples:
- Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine and sertraline are effective for depression but can lead to decreased libido and difficulty achieving orgasm.
- Antihypertensives: Medications for high blood pressure, such as beta-blockers and diuretics, may cause erectile dysfunction or reduced sexual desire.
- Antipsychotics: Drugs like risperidone can lead to hormonal changes that affect sexual function, including reduced libido and erectile issues.
- Opioids: Chronic use of pain medications can lead to hormonal imbalances, resulting in decreased sexual desire and performance.
Statistics and Case Studies
Research indicates that sexual dysfunction is a common side effect of many medications. A study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine found that approximately 30% of patients taking antidepressants reported sexual side effects. Another study revealed that nearly 50% of men on antihypertensive medications experienced erectile dysfunction.
Case studies also highlight the impact of medication on sexual function. For instance, a 45-year-old male patient on SSRIs for depression reported a significant decrease in libido and difficulty achieving orgasm, leading to relationship strain. After discussing these side effects with his healthcare provider, he was switched to a different class of antidepressants with fewer sexual side effects, resulting in improved sexual function.
Strategies for Managing Medication-Related Sexual Dysfunction
Patients experiencing sexual dysfunction due to medication should consider the following strategies:
- Open Communication: Discuss any sexual side effects with your healthcare provider. They can help assess the situation and suggest alternatives.
- Medication Review: Regularly review all medications with your doctor to identify potential culprits and explore alternatives.
- Timing Adjustments: Sometimes, adjusting the timing of medication intake can help mitigate side effects.
- Therapy and Counseling: Engaging in therapy can help address psychological factors contributing to sexual dysfunction.
Conclusion
Understanding the impact of medication on sexual function is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. By recognizing the potential side effects of various medications, patients can take proactive steps to manage their sexual health. Open communication with healthcare providers, regular medication reviews, and exploring alternative treatments can significantly improve sexual function. Ultimately, prioritizing sexual health is a vital aspect of holistic care, ensuring that individuals can lead fulfilling lives both physically and emotionally.