-
Table of Contents
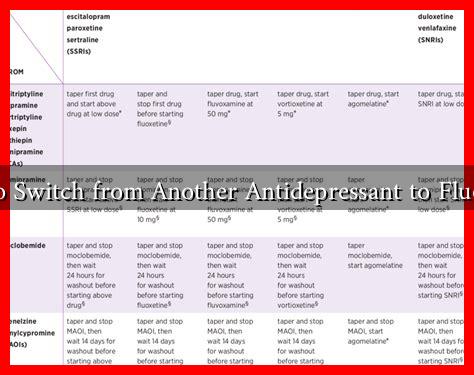
How to Switch from Another Antidepressant to Fluoxetine
Switching antidepressants can be a daunting process, especially when transitioning to a specific medication like fluoxetine (commonly known as Prozac). Fluoxetine is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that is widely prescribed for depression, anxiety disorders, and other mental health conditions. This article will guide you through the process of switching to fluoxetine, highlighting important considerations, potential side effects, and best practices for a smooth transition.
Understanding Fluoxetine
Fluoxetine was first approved by the FDA in 1987 and has since become one of the most commonly prescribed antidepressants. It works by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, which can help improve mood and emotional well-being. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately 7.8% of adults in the U.S. experience depression, and fluoxetine is often a first-line treatment option.
Reasons for Switching Antidepressants
There are several reasons why a patient might consider switching to fluoxetine:
- Ineffectiveness: The current antidepressant may not be providing the desired relief from symptoms.
- Side Effects: Unpleasant side effects from the current medication may lead to a decision to switch.
- New Diagnosis: A change in diagnosis may necessitate a different treatment approach.
- Personal Preference: Some patients may prefer fluoxetine due to its long history of use and established efficacy.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider
Before making any changes to your medication regimen, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider. They will assess your current treatment plan and discuss the potential benefits and risks of switching to fluoxetine. Here are some key points to consider during your consultation:
- Current Medication: Provide a complete list of your current medications, including dosages and duration of use.
- Medical History: Discuss any past experiences with antidepressants, including side effects and effectiveness.
- Symptoms: Be open about your current symptoms and how they impact your daily life.
Transitioning to Fluoxetine
The process of switching to fluoxetine typically involves a gradual tapering of the current antidepressant, followed by the introduction of fluoxetine. This method helps minimize withdrawal symptoms and potential side effects. Here’s a general outline of the transition process:
- Tapering Off: Your doctor may recommend gradually reducing the dosage of your current antidepressant over several weeks.
- Starting Fluoxetine: Once you have tapered off the previous medication, your doctor will prescribe fluoxetine, usually starting at a low dose (e.g., 20 mg per day).
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments will be necessary to monitor your response to fluoxetine and adjust the dosage as needed.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Like all medications, fluoxetine can cause side effects. Common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Insomnia
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Sexual dysfunction
It is essential to report any severe or persistent side effects to your healthcare provider. Additionally, be aware of the potential for serotonin syndrome, a rare but serious condition that can occur when combining certain medications.
Case Studies and Statistics
Research indicates that fluoxetine is effective for many patients. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that fluoxetine was effective in treating major depressive disorder in 60-70% of patients. Furthermore, a case study involving a patient who switched from sertraline to fluoxetine reported significant improvement in depressive symptoms within four weeks of starting fluoxetine.
Conclusion
Switching from another antidepressant to fluoxetine can be a beneficial step for many individuals struggling with depression or anxiety. By consulting with your healthcare provider, tapering off your current medication, and closely monitoring your response to fluoxetine, you can navigate this transition effectively. Remember that each person’s experience with antidepressants is unique, and finding the right medication may take time. Stay informed, be patient, and prioritize open communication with your healthcare team to achieve the best possible outcome.