-
Table of Contents
How is Azithromycin Prescribed for COVID-19?
As the world grappled with the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers and healthcare professionals explored various treatment options to mitigate the effects of the virus. One such medication that gained attention was Azithromycin, an antibiotic primarily used to treat bacterial infections. This article delves into how Azithromycin is prescribed for COVID-19, its efficacy, and the controversies surrounding its use.
Understanding Azithromycin
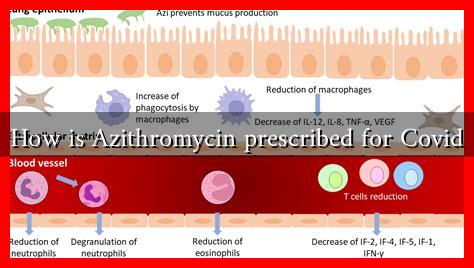
Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, thereby stopping the growth of bacteria. It is commonly prescribed for respiratory infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. Its anti-inflammatory properties also make it a candidate for treating viral infections, including COVID-19.
The Role of Azithromycin in COVID-19 Treatment
During the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic, Azithromycin was considered for use in treating COVID-19 due to its potential anti-inflammatory effects and its ability to combat secondary bacterial infections that could arise in patients with viral infections.
Prescribing Guidelines
Azithromycin is not a first-line treatment for COVID-19. However, it may be prescribed in specific scenarios:
- Secondary Bacterial Infections: If a patient develops a bacterial infection alongside COVID-19, Azithromycin may be prescribed to treat that infection.
- High-Risk Patients: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe Azithromycin to high-risk patients who are at greater risk of developing complications from COVID-19.
- Clinical Trials: Azithromycin has been included in various clinical trials to assess its efficacy in treating COVID-19, and prescriptions may be part of these studies.
Controversies and Efficacy
The use of Azithromycin for COVID-19 has been met with mixed reviews. Initial studies suggested potential benefits, but subsequent research has raised questions about its effectiveness:
- Early Studies: Some early studies indicated that Azithromycin could reduce viral load and improve clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
- Later Research: More comprehensive studies, including randomized controlled trials, have shown little to no significant benefit of Azithromycin in treating COVID-19 compared to standard care.
- Guidelines from Health Authorities: Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have cautioned against the routine use of Azithromycin for COVID-19 outside of clinical trials.
Case Studies and Statistics
Several case studies have been published regarding the use of Azithromycin in COVID-19 treatment:
- Study in France: A study led by Dr. Didier Raoult in France suggested that Azithromycin, when combined with hydroxychloroquine, could be effective in treating COVID-19. However, this study faced criticism for its methodology and lack of peer review.
- Randomized Trials: A large-scale randomized trial conducted by the RECOVERY trial group in the UK found no significant benefit of Azithromycin in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
- Statistics: According to a meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), the use of Azithromycin did not significantly reduce mortality or the need for mechanical ventilation in COVID-19 patients.
Conclusion
While Azithromycin has been prescribed in certain cases for COVID-19, its role remains controversial and is not widely endorsed as a treatment option. The initial enthusiasm surrounding its use has been tempered by subsequent research that has shown limited efficacy. Healthcare providers must weigh the potential benefits against the risks and adhere to guidelines set forth by health authorities. As the pandemic evolves, ongoing research will continue to shape our understanding of effective treatments for COVID-19.
For more information on COVID-19 treatments and guidelines, you can visit the CDC’s official website.