-
Table of Contents
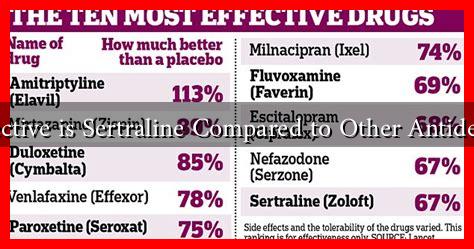
- How Effective is Sertraline Compared to Other Antidepressants?
- Understanding Sertraline and Its Mechanism of Action
- Comparative Effectiveness of Sertraline
- Clinical Evidence Supporting Sertraline’s Efficacy
- Side Effects and Tolerability
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- Conclusion: Key Takeaways
How Effective is Sertraline Compared to Other Antidepressants?
Sertraline, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), is one of the most commonly prescribed antidepressants worldwide. It is primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder. This article explores the effectiveness of sertraline compared to other antidepressants, examining its benefits, drawbacks, and overall impact on mental health.
Understanding Sertraline and Its Mechanism of Action
Sertraline works by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in mood regulation. By inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, sertraline helps to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. Its efficacy has been supported by numerous clinical trials, making it a first-line treatment option for many mental health conditions.
Comparative Effectiveness of Sertraline
When evaluating the effectiveness of sertraline, it is essential to compare it with other classes of antidepressants, including:
- Other SSRIs: Medications like fluoxetine (Prozac) and escitalopram (Lexapro) are also SSRIs and share similar mechanisms of action.
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): Drugs such as venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta) target both serotonin and norepinephrine.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): Older medications like amitriptyline and nortriptyline are less commonly prescribed due to their side effect profiles.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): These are effective but require dietary restrictions and careful monitoring.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Sertraline’s Efficacy
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of sertraline in treating depression and anxiety. For instance, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found that sertraline was significantly more effective than placebo in reducing depressive symptoms. The study highlighted that approximately 60-70% of patients experienced a meaningful reduction in symptoms after 12 weeks of treatment.
In comparison to other SSRIs, sertraline has shown similar efficacy. A study published in The American Journal of Psychiatry indicated that sertraline was as effective as fluoxetine and escitalopram, with a comparable side effect profile. However, some patients may respond better to one SSRI over another, emphasizing the need for personalized treatment plans.
Side Effects and Tolerability
While sertraline is generally well-tolerated, it is not without side effects. Common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Insomnia
- Sexual dysfunction
- Weight gain
- Dry mouth
In comparison, SNRIs may cause increased blood pressure, while TCAs are associated with more severe side effects, such as sedation and anticholinergic effects. The tolerability of sertraline makes it a preferred choice for many patients, especially those who may be sensitive to the side effects of other antidepressants.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Case studies provide valuable insights into the real-world effectiveness of sertraline. For example, a 35-year-old woman with generalized anxiety disorder experienced significant improvement in her symptoms after starting sertraline, reporting a 50% reduction in anxiety levels within six weeks. In contrast, a 40-year-old man with major depressive disorder found that venlafaxine was more effective for his symptoms, highlighting the variability in individual responses to antidepressants.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
Sertraline is a highly effective antidepressant that has been proven to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety in many patients. Its efficacy is comparable to other SSRIs and SNRIs, making it a valuable option in the treatment landscape. However, individual responses to medication can vary significantly, necessitating personalized treatment approaches. While sertraline is generally well-tolerated, healthcare providers must consider potential side effects and patient preferences when prescribing antidepressants.
In summary, sertraline stands out as an effective treatment for depression and anxiety, but the choice of antidepressant should always be tailored to the individual, taking into account their unique symptoms, medical history, and response to previous treatments.