-
Table of Contents
How Does Valsartan Work in the Body?
Valsartan is a medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart failure. As a member of the angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) class of drugs, it plays a crucial role in managing cardiovascular health. This article delves into the mechanisms of action of Valsartan, its therapeutic uses, and its impact on the body.
Understanding Valsartan
Valsartan is an oral medication that helps relax blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood. It is often prescribed for patients who have hypertension or are at risk of heart failure. The drug is marketed under various brand names, with Diovan being one of the most recognized.
Mechanism of Action
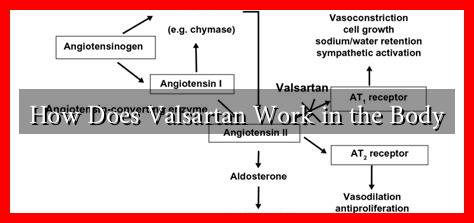
Valsartan works by blocking the action of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor that plays a significant role in regulating blood pressure. Here’s how it functions:
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockade: Valsartan selectively binds to the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor, preventing angiotensin II from exerting its effects.
- Vasodilation: By blocking the AT1 receptor, Valsartan causes blood vessels to relax and widen, which lowers blood pressure.
- Reduced Aldosterone Secretion: Angiotensin II stimulates the secretion of aldosterone, a hormone that promotes sodium and water retention. Valsartan reduces aldosterone levels, leading to decreased fluid volume and lower blood pressure.
This multi-faceted approach not only helps in lowering blood pressure but also reduces the workload on the heart, making it an effective treatment for heart failure.
Therapeutic Uses of Valsartan
Valsartan is primarily used for:
- Hypertension: It is effective in lowering high blood pressure, which can reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack, and kidney problems.
- Heart Failure: Valsartan is used to improve survival rates in patients with heart failure and to reduce hospitalizations.
- Post-Myocardial Infarction: It is prescribed to patients who have recently suffered a heart attack to improve outcomes and prevent further complications.
Case Studies and Statistics
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Valsartan in managing hypertension and heart failure. For instance, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that Valsartan significantly reduced blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension compared to placebo.
Another study highlighted that patients with heart failure who were treated with Valsartan had a 20% reduction in mortality rates compared to those receiving standard care. These findings underscore the importance of Valsartan in improving patient outcomes in cardiovascular health.
Potential Side Effects
While Valsartan is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea
In rare cases, it may lead to more severe side effects, including kidney problems or allergic reactions. Patients are advised to consult their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual symptoms.
Conclusion
Valsartan is a vital medication in the management of hypertension and heart failure, working primarily through the blockade of angiotensin II receptors. Its ability to lower blood pressure and reduce the strain on the heart makes it an essential tool in cardiovascular therapy. With a solid foundation of research supporting its efficacy and safety, Valsartan continues to be a cornerstone in the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions.
In summary, understanding how Valsartan works in the body not only helps patients manage their conditions more effectively but also empowers them to engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers about their treatment options.