-
Table of Contents
How Does Rising Temperature Influence Fall Agriculture?
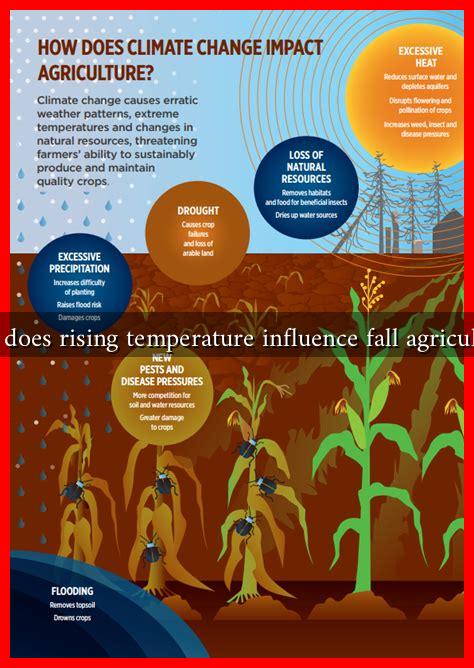
As global temperatures continue to rise due to climate change, the agricultural sector faces unprecedented challenges and opportunities. Fall agriculture, which includes the cultivation of crops such as corn, soybeans, and pumpkins, is particularly affected by these temperature changes. Understanding how rising temperatures influence fall agriculture is crucial for farmers, policymakers, and consumers alike.
The Impact of Rising Temperatures on Crop Growth
Temperature plays a vital role in the growth and development of crops. Each plant species has an optimal temperature range for growth, and deviations from this range can lead to various consequences:
- Accelerated Growth Rates: Warmer temperatures can lead to faster growth rates in some crops. For instance, studies have shown that corn can mature more quickly in warmer conditions, potentially allowing for an extended growing season.
- Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: Higher temperatures can create favorable conditions for pests and diseases. For example, the corn earworm, a significant pest for corn farmers, thrives in warmer climates, leading to increased crop damage.
- Altered Pollination: Temperature changes can affect the timing of flowering and pollination. For crops like pumpkins, which rely on specific pollinators, this can lead to reduced yields if pollination occurs at suboptimal times.
Case Studies: Regional Variations in Fall Agriculture
The effects of rising temperatures on fall agriculture are not uniform across regions. Different areas experience varying impacts based on local climate conditions, soil types, and agricultural practices. Here are a few case studies:
- The Midwest United States: In states like Iowa and Illinois, rising temperatures have led to longer growing seasons. Farmers have reported increased yields for corn and soybeans, but they also face challenges such as drought and increased pest populations.
- California: In California, where fall agriculture includes crops like grapes and nuts, rising temperatures have led to earlier harvests. However, the state also faces water scarcity issues, which are exacerbated by higher temperatures.
- Canada: In regions like the Prairie Provinces, warmer temperatures have allowed farmers to grow crops that were previously unsuitable for the climate, such as soybeans and canola. This shift presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of market competition and crop management.
Adapting to Climate Change: Strategies for Farmers
As temperatures continue to rise, farmers must adapt their practices to mitigate the impacts on fall agriculture. Here are some strategies that can be employed:
- Crop Diversification: By planting a variety of crops, farmers can reduce their risk of total crop failure due to temperature fluctuations or pest outbreaks.
- Improved Irrigation Techniques: Implementing efficient irrigation systems can help manage water resources more effectively, especially in regions facing drought.
- Utilizing Heat-Resistant Varieties: Breeding and selecting crop varieties that are more tolerant to heat can help maintain yields in warmer conditions.
Statistics and Projections
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), global temperatures are projected to rise by 1.5°C to 2°C by the end of the century if current trends continue. This increase could lead to significant changes in agricultural productivity:
- Yields for staple crops like wheat and rice could decline by up to 25% in some regions.
- Increased frequency of extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, could disrupt planting and harvesting schedules.
Conclusion: Preparing for the Future of Fall Agriculture
Rising temperatures present both challenges and opportunities for fall agriculture. While some regions may benefit from longer growing seasons and increased yields, others may face significant risks from pests, diseases, and water scarcity. It is essential for farmers to adopt adaptive strategies to mitigate these impacts and ensure food security in a changing climate. As we move forward, collaboration among farmers, researchers, and policymakers will be crucial in developing sustainable agricultural practices that can withstand the challenges posed by climate change.
For more information on climate change and its impact on agriculture, you can visit the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).