-
Table of Contents
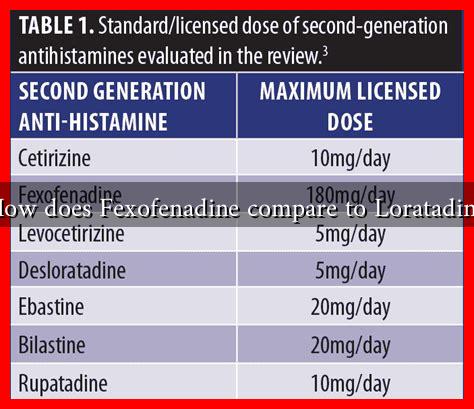
How Does Fexofenadine Compare to Loratadine?
Allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, affects millions of people worldwide, leading to symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes. Antihistamines are a popular choice for managing these symptoms, with Fexofenadine and Loratadine being two of the most commonly used options. This article explores the differences and similarities between these two medications, helping you make an informed choice for allergy relief.
Understanding Fexofenadine and Loratadine
Both Fexofenadine and Loratadine belong to a class of medications known as second-generation antihistamines. They are designed to alleviate allergy symptoms with fewer sedative effects compared to first-generation antihistamines like diphenhydramine.
- Fexofenadine: Marketed under the brand name Allegra, Fexofenadine is effective in treating seasonal allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria (hives).
- Loratadine: Known by the brand name Claritin, Loratadine is also used for seasonal allergic rhinitis and is available over-the-counter.
Mechanism of Action
Both medications work by blocking the action of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic symptoms. However, their pharmacokinetics—how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes the drug—differ slightly.
- Fexofenadine: It is rapidly absorbed and reaches peak plasma concentrations within 2 to 3 hours. It is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine.
- Loratadine: This medication is metabolized in the liver to its active form, desloratadine, which also has antihistaminic properties. Peak plasma concentrations occur within 1 to 2 hours.
Efficacy in Treating Allergies
Clinical studies have shown that both Fexofenadine and Loratadine are effective in reducing allergy symptoms, but there are nuances in their efficacy.
- Fexofenadine: Research indicates that Fexofenadine may provide faster relief from symptoms, particularly nasal congestion, compared to Loratadine. A study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that patients reported significant improvement in symptoms within hours of taking Fexofenadine.
- Loratadine: While effective, Loratadine may take longer to show results, with some patients experiencing relief after a few hours. However, it is often preferred for its longer duration of action, allowing for once-daily dosing.
Side Effects and Safety
Both medications are generally well-tolerated, but they do have potential side effects.
- Fexofenadine: Common side effects include headache, dizziness, and gastrointestinal disturbances. It is less likely to cause sedation compared to first-generation antihistamines.
- Loratadine: Similar side effects can occur, with headache and fatigue being the most reported. Loratadine is also considered non-sedating, making it suitable for daytime use.
Cost and Availability
Both Fexofenadine and Loratadine are available over-the-counter, making them accessible options for allergy sufferers. However, pricing can vary based on brand and formulation.
- Fexofenadine: Typically priced higher than Loratadine, especially for brand-name versions.
- Loratadine: Often available in generic forms, making it a more cost-effective choice for many consumers.
Conclusion
In summary, both Fexofenadine and Loratadine are effective second-generation antihistamines that provide relief from allergy symptoms. Fexofenadine may offer faster relief, particularly for nasal congestion, while Loratadine is often favored for its longer duration of action and cost-effectiveness. Ultimately, the choice between the two may depend on individual preferences, specific symptoms, and consultation with a healthcare provider. Always consider discussing your options with a medical professional to determine the best treatment plan for your allergy symptoms.