-
Table of Contents
How Does Azithromycin Impact Bacterial Resistance?
Azithromycin, a widely used macrolide antibiotic, has been a cornerstone in the treatment of various bacterial infections since its introduction in the late 1980s. While it is effective against a range of pathogens, its impact on bacterial resistance is a growing concern in the medical community. This article explores how azithromycin influences bacterial resistance, the mechanisms behind it, and the implications for public health.
The Mechanism of Action of Azithromycin
Azithromycin works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. It binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit of bacteria, preventing the translation of mRNA into proteins essential for bacterial growth and reproduction. This mechanism makes it effective against a variety of gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria, as well as atypical pathogens.
Understanding Bacterial Resistance
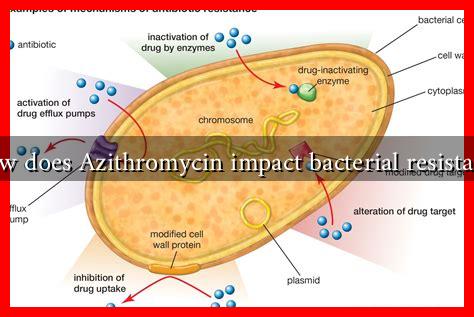
Bacterial resistance occurs when bacteria evolve to survive exposure to antibiotics that once effectively killed them. This resistance can arise through various mechanisms, including:
- Genetic Mutation: Spontaneous mutations in bacterial DNA can confer resistance.
- Horizontal Gene Transfer: Bacteria can acquire resistance genes from other bacteria through transformation, transduction, or conjugation.
- Efflux Pumps: Some bacteria develop pumps that expel antibiotics before they can exert their effects.
Azithromycin and Resistance Development
Research indicates that the use of azithromycin can lead to increased rates of resistance among certain bacterial populations. This phenomenon is particularly evident in respiratory pathogens and sexually transmitted infections. Key points include:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae: Studies have shown that the overuse of azithromycin has led to a rise in resistance among strains of S. pneumoniae, complicating treatment options for pneumonia and other infections.
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Azithromycin is often used to treat gonorrhea, but resistance has been documented, leading to treatment failures in some cases.
- Mycobacterium avium complex: In patients with HIV/AIDS, prolonged azithromycin use has been associated with the emergence of resistant strains.
Case Studies and Statistics
A study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy highlighted the alarming rise in azithromycin resistance among S. pneumoniae in the United States. The study found that resistance rates increased from 0% in 1999 to over 30% by 2018. This trend poses significant challenges for treating respiratory infections, particularly in vulnerable populations.
Another case study focused on the treatment of gonorrhea, where azithromycin was part of dual therapy. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that resistance to azithromycin among N. gonorrhoeae strains rose from 0.6% in 2013 to 2.6% in 2017, indicating a worrying trend that could lead to treatment failures.
Public Health Implications
The rise of azithromycin resistance has significant implications for public health, including:
- Increased Treatment Failures: As resistance rates climb, the effectiveness of azithromycin diminishes, leading to higher rates of treatment failures.
- Higher Healthcare Costs: Treating resistant infections often requires more expensive and potent antibiotics, increasing the financial burden on healthcare systems.
- Spread of Resistance: Resistant strains can spread within communities, making infections harder to control and treat.
Conclusion
Azithromycin remains a vital tool in the fight against bacterial infections, but its impact on bacterial resistance cannot be overlooked. The increasing rates of resistance among key pathogens highlight the need for prudent antibiotic use and ongoing surveillance. Public health initiatives must focus on educating healthcare providers and patients about the responsible use of antibiotics to mitigate the rise of resistance. As we continue to rely on azithromycin and other antibiotics, understanding and addressing the factors contributing to resistance will be crucial in preserving their effectiveness for future generations.