-
Table of Contents
The Impact of Flood Zones in Florida
Florida, known for its beautiful beaches and sunny weather, is also notorious for its vulnerability to flooding. With a large portion of the state lying at or below sea level, Florida is particularly susceptible to the effects of rising sea levels and extreme weather events. Understanding flood zones in Florida is crucial for residents, businesses, and policymakers to mitigate risks and protect property.
What are Flood Zones?
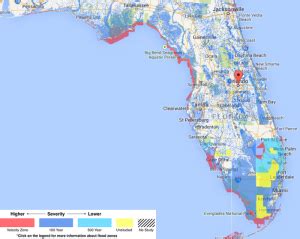
Flood zones are geographic areas that are prone to flooding based on historical data and analysis. In Florida, flood zones are classified by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) into different categories based on the likelihood of flooding. These zones are crucial for determining Insurance rates, building regulations, and emergency response planning.
FEMA Flood Zone Categories
- Zone A: Areas with a 1% annual chance of flooding.
- Zone AE: Areas with a 1% annual chance of flooding and additional hazards.
- Zone X: Areas with minimal risk of flooding.
The Impact of Flood Zones in Florida
Florida’s unique Geography and climate make it particularly vulnerable to flooding. With over 1,300 miles of coastline, Florida is at risk of storm surges, heavy rainfall, and sea-level rise. According to FEMA, Florida has the highest number of properties at risk of flooding in the United States.
Case Study: Miami-Dade County
Miami-Dade County, located in Southeast Florida, is one of the most flood-prone areas in the state. With a large population and extensive infrastructure, the county faces significant challenges in managing flood risks. In recent years, Miami-Dade has experienced increased flooding due to sea-level rise and extreme weather events.
Statistics:
- Over 300,000 properties in Miami-Dade County are located in FEMA-designated flood zones.
- Sea levels in Miami have risen by over 9 inches since 1900, increasing the risk of coastal flooding.
Managing Flood Risks in Florida
Given the high risk of flooding in Florida, it is essential for residents and policymakers to take proactive measures to mitigate risks and protect property. This includes investing in flood insurance, implementing building codes, and promoting sustainable development practices.
Resources:
- For information on flood insurance in Florida, visit FloodSmart.gov.
- For building regulations in flood zones, consult your local building department or FEMA guidelines.
Conclusion
Florida’s flood zones pose significant challenges for residents and policymakers, but with proper planning and mitigation efforts, the risks can be minimized. By understanding flood zones, investing in flood insurance, and implementing sustainable practices, Florida can better prepare for future flooding events and protect its communities.