-
Table of Contents
- Optimizing Fermentation for Bio-Ethanol Production
- The Role of Fermentation in Bio-Ethanol Production
- Factors Influencing Fermentation
- Temperature
- pH
- Nutrient Availability
- Oxygen Levels
- Microorganism Strain
- Optimizing Fermentation for Bio-Ethanol Production
- Case Study: Optimizing Fermentation in a Bio-Ethanol Plant
- Conclusion
Optimizing Fermentation for Bio-Ethanol Production
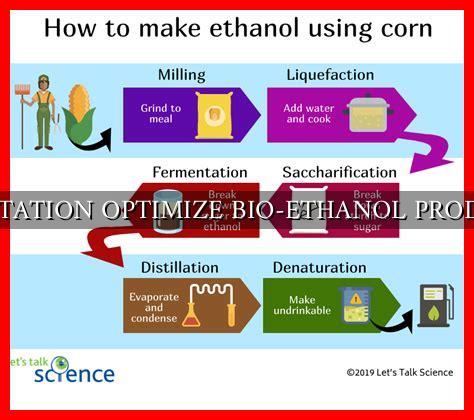
Fermentation is a crucial process in the production of bio-ethanol, a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. By optimizing fermentation conditions, we can increase the efficiency and yield of bio-ethanol production. In this article, we will explore the key factors that influence fermentation and how they can be optimized to enhance bio-ethanol production.
The Role of Fermentation in Bio-Ethanol Production
Fermentation is the process by which microorganisms, such as yeast or bacteria, convert sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide. In bio-ethanol production, fermentation is a key step that determines the yield and quality of the final product. By controlling fermentation conditions, we can maximize ethanol production while minimizing by-products and waste.
Factors Influencing Fermentation
Several factors influence the fermentation process, including:
- Temperature
- pH
- Nutrient availability
- Oxygen levels
- Microorganism strain
Temperature
Temperature plays a critical role in fermentation as it affects the growth and activity of microorganisms.
. Most fermentation processes occur at temperatures between 25-35°C, depending on the strain of microorganism used. By maintaining optimal temperature conditions, we can ensure efficient fermentation and maximize ethanol production.
pH
pH levels also impact fermentation as they influence the activity of enzymes and microorganisms. The optimal pH for ethanol fermentation is typically around 4.0-5.0. By adjusting and monitoring pH levels during fermentation, we can create an environment that is conducive to ethanol production.
Nutrient Availability
Microorganisms require nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and vitamins to thrive and produce ethanol. By providing the necessary nutrients in the right proportions, we can promote the growth and activity of microorganisms, leading to increased ethanol production.
Oxygen Levels
Oxygen is essential for the growth of yeast during the initial stages of fermentation. However, excessive oxygen can inhibit ethanol production. By controlling oxygen levels during fermentation, we can strike a balance that promotes yeast growth while maximizing ethanol production.
Microorganism Strain
The choice of microorganism strain can significantly impact fermentation efficiency and ethanol yield. Different strains of yeast or bacteria have varying abilities to convert sugars into ethanol. By selecting a strain that is well-suited to the fermentation conditions, we can optimize ethanol production.
Optimizing Fermentation for Bio-Ethanol Production
To optimize fermentation for bio-ethanol production, it is essential to:
- Monitor and control temperature, pH, and nutrient levels throughout the fermentation process.
- Select a suitable microorganism strain that is well-adapted to the fermentation conditions.
- Minimize oxygen exposure during fermentation to maximize ethanol production.
- Regularly test and adjust fermentation conditions to ensure optimal ethanol yield.
Case Study: Optimizing Fermentation in a Bio-Ethanol Plant
In a study conducted at a bio-ethanol plant, researchers optimized fermentation conditions by closely monitoring temperature, pH, and nutrient levels. By implementing these changes, they were able to increase ethanol production by 20% while reducing by-product formation. This case study demonstrates the importance of optimizing fermentation for bio-ethanol production.
Conclusion
Optimizing fermentation is essential for maximizing bio-ethanol production efficiency and yield. By controlling factors such as temperature, pH, nutrient availability, oxygen levels, and microorganism strain, we can enhance ethanol production while minimizing waste. Through careful monitoring and adjustment of fermentation conditions, we can create a more sustainable and efficient bio-ethanol production process.