-
Table of Contents
FAT VS SATURATED FAT: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to nutrition, fats often get a bad rap. However, not all fats are created equal. In fact, there is a distinct difference between fats and saturated fats, each playing a unique role in our overall health. In this article, we will delve into the differences between fat and saturated fat, their effects on the body, and how to make informed choices when it comes to incorporating them into our diets.
What is Fat?
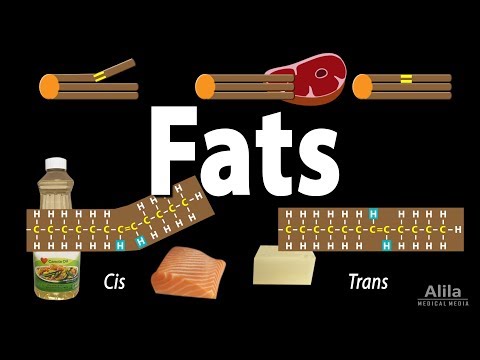
Fat is an essential macronutrient that provides energy, supports cell growth, and helps the body absorb certain vitamins. There are different types of fats, including unsaturated fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) and saturated fats.
. Unsaturated fats are considered healthy fats and can be found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. On the other hand, saturated fats are often associated with negative health outcomes when consumed in excess.
What is Saturated Fat?
Saturated fat is a type of fat that is solid at room temperature and is commonly found in animal products like meat and dairy, as well as in processed foods like baked goods and fried foods. Consuming too much saturated fat has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, as it can raise levels of LDL cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol) in the blood.
The Role of Fat and Saturated Fat in the Body
While both fat and saturated fat play important roles in the body, it is crucial to consume them in moderation and make healthy choices. Here are some key points to consider:
- Fat is a concentrated source of energy, providing 9 calories per gram.
- Saturated fat should be limited to less than 10% of total daily calories to reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats can have a positive impact on heart health.
Making Informed Choices
When it comes to incorporating fats into your diet, it is important to make informed choices. Opt for healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, and limit your intake of saturated fats from sources like red meat and processed foods. Reading nutrition labels can help you identify the types of fats in packaged foods and make healthier choices.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between fat and saturated fat is essential for making informed decisions about your diet and overall health. While fat is a necessary nutrient that provides energy and supports various bodily functions, saturated fat should be consumed in moderation to reduce the risk of heart disease. By choosing healthy fats and limiting saturated fats, you can support your overall well-being and maintain a balanced diet.
For more information on fats and nutrition, check out this resource.