-
Table of Contents
Event Driven Architecture with Kafka: Revolutionizing Data Processing
Event Driven Architecture (EDA) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for building scalable and resilient systems that can react to events in real-time. Kafka, an open-source distributed event streaming platform, has become the de facto standard for implementing EDA. In this article, we will explore the key concepts of Event Driven Architecture with Kafka and how it is revolutionizing data processing.
What is Event Driven Architecture?
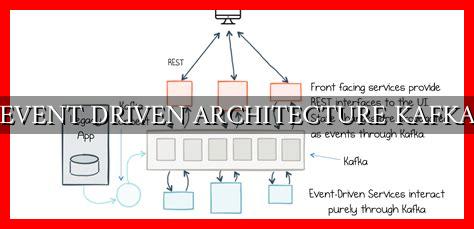
Event Driven Architecture is a design pattern that decouples system components by using events to trigger and communicate changes. In EDA, events are the building blocks of the system, representing state changes or updates that are propagated asynchronously to interested parties. This allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and responsiveness in handling complex workflows.
Key Components of Event Driven Architecture
- Event Producer: Generates events and publishes them to a central event bus.
- Event Bus: Acts as a message broker that routes events to interested consumers.
- Event Consumer: Subscribes to events from the event bus and processes them accordingly.
Why Kafka for Event Driven Architecture?
Kafka provides a distributed, fault-tolerant, and scalable platform for building event-driven systems.
. It offers high throughput, low latency, and strong durability guarantees, making it ideal for processing large volumes of data in real-time. Kafka’s architecture is based on topics, partitions, and consumer groups, allowing for efficient event distribution and processing.
Real-World Use Cases
Many organizations across various industries have adopted Kafka for implementing Event Driven Architecture. For example, Uber uses Kafka to process millions of events per second for real-time analytics and monitoring. Netflix leverages Kafka for event sourcing and stream processing to deliver personalized recommendations to users. These use cases demonstrate the versatility and scalability of Kafka in handling diverse workloads.
Benefits of Event Driven Architecture with Kafka
- Scalability: Kafka’s distributed nature allows for horizontal scaling to handle increasing event volumes.
- Resilience: Kafka provides fault tolerance and data replication to ensure high availability and data integrity.
- Real-time Processing: Events are processed in near real-time, enabling timely insights and actions.
- Flexibility: EDA with Kafka supports event-driven microservices, enabling modular and decoupled architectures.
Conclusion
Event Driven Architecture with Kafka is transforming the way organizations process and react to data. By leveraging Kafka’s capabilities for event streaming, organizations can build scalable, resilient, and real-time systems that drive innovation and competitive advantage. As more businesses embrace EDA with Kafka, we can expect to see further advancements in data processing and analytics.
For more information on Kafka and Event Driven Architecture, visit https://kafka.apache.org/.