-
Table of Contents
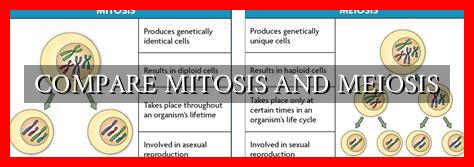
Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
Cell division is a fundamental process in all living organisms, essential for growth, repair, and reproduction. Two main types of cell division are mitosis and meiosis, each serving distinct purposes in the life cycle of an organism. In this article, we will compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis, highlighting their key differences and similarities.
Mitosis: The Basis of Growth and Repair
Mitosis is a type of cell division that occurs in somatic cells, leading to the production of two identical daughter cells. This process is crucial for growth, tissue repair, and maintenance of the body’s cells. Mitosis consists of several stages, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, where the chromosomes are replicated and segregated into two daughter cells.
- Prophase: Chromosomes condense and become visible under a microscope.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the cell’s equator.
- Anaphase: Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles.
- Telophase: Chromosomes decondense, and two new nuclei form.
One key characteristic of mitosis is that it results in genetically identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
. This ensures that the genetic information is faithfully passed on during cell division.
Meiosis: The Basis of Sexual Reproduction
Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in germ cells, leading to the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells). Unlike mitosis, meiosis involves two rounds of cell division, resulting in four haploid daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Meiosis I: Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material in a process called crossing over.
- Meiosis II: Sister chromatids separate, resulting in four haploid daughter cells.
Meiosis introduces genetic diversity through the shuffling of genetic material during crossing over and the random assortment of chromosomes during cell division. This genetic variation is essential for evolution and adaptation in sexually reproducing organisms.
Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
While mitosis and meiosis are both essential for the life cycle of organisms, they have several key differences:
- Number of divisions: Mitosis involves one division, while meiosis involves two divisions.
- Genetic content: Mitosis produces two diploid daughter cells, while meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells.
- Purpose: Mitosis is for growth and repair, while meiosis is for sexual reproduction.
- Genetic variation: Meiosis introduces genetic diversity through crossing over and random assortment of chromosomes.
Understanding the differences between mitosis and meiosis is crucial for comprehending the complexity of cell division and its role in the life cycle of organisms. Both processes are tightly regulated and ensure the proper transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mitosis and meiosis are two distinct types of cell division with specific roles in the life cycle of organisms. While mitosis is essential for growth and repair, meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. By comparing and contrasting these two processes, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexity of cell division and its significance in the evolution of life on Earth.
For further reading on the topic, you can explore this resource from Khan Academy.