-
Table of Contents
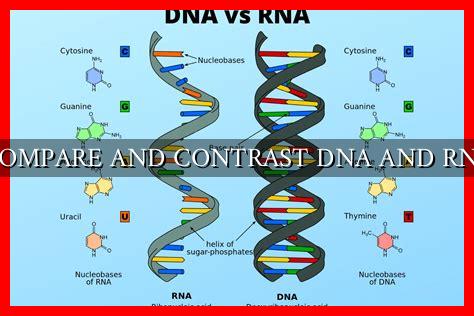
Compare and Contrast DNA and RNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are two essential molecules that play a crucial role in the functioning of living organisms. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct differences that set them apart. In this article, we will compare and contrast DNA and RNA to understand their structures, functions, and significance in biological processes.
Structure
One of the key differences between DNA and RNA lies in their structure. DNA is a double-stranded molecule that forms a double helix, consisting of two complementary strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases. The four bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
On the other hand, RNA is typically single-stranded and does not form a double helix like DNA.
. RNA contains the bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), but instead of thymine, it has uracil (U) as a complementary base to adenine. This structural difference allows RNA to perform various functions that DNA cannot.
Function
DNA serves as the genetic blueprint of an organism, containing the instructions for the development, growth, and functioning of cells. It carries the genetic information that is passed down from one generation to the next. DNA replication is a crucial process that ensures the faithful transmission of genetic material during cell division.
RNA, on the other hand, plays a diverse range of roles in the cell. It is involved in protein synthesis, gene expression, and regulation of gene activity. There are several types of RNA, including messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), each with specific functions in the cell.
Significance
Both DNA and RNA are essential for the survival and functioning of living organisms. Without DNA, cells would not be able to replicate and pass on genetic information to offspring. RNA plays a crucial role in translating the genetic code into proteins, which are the building blocks of cells and tissues.
- DNA is stable and less prone to mutations compared to RNA.
- RNA is more versatile and can perform a wider range of functions than DNA.
- Both DNA and RNA are composed of nucleotides, but they differ in their sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DNA and RNA are two fundamental molecules that are essential for life. While they share some similarities, such as being composed of nucleotides and carrying genetic information, they also have distinct differences in their structure, function, and significance. Understanding the roles of DNA and RNA in biological processes is crucial for advancing our knowledge of genetics and molecular biology.
For further reading on the topic, you can explore this resource from the National Center for Biotechnology Information.