-
Table of Contents
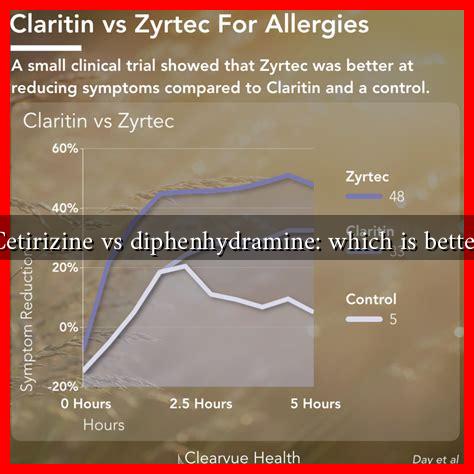
Cetirizine vs Diphenhydramine: Which is Better?
Allergies can be a significant nuisance, affecting millions of people worldwide. When it comes to managing allergy symptoms, two popular over-the-counter antihistamines often come into play: cetirizine and diphenhydramine. Both medications are effective in alleviating symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes, but they differ in their mechanisms, side effects, and overall effectiveness. This article will explore the differences between cetirizine and diphenhydramine to help you determine which is better for your needs.
Understanding Antihistamines
Antihistamines are drugs that counteract the effects of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic symptoms. They are classified into two categories: first-generation and second-generation antihistamines.
- First-Generation Antihistamines: These include diphenhydramine and are known for their sedative effects. They can cross the blood-brain barrier, leading to drowsiness.
- Second-Generation Antihistamines: Cetirizine falls into this category. These medications are less likely to cause sedation as they do not readily cross the blood-brain barrier.
Cetirizine: The Non-Sedating Option
Cetirizine, commonly known by its brand name Zyrtec, is a second-generation antihistamine that is effective in treating allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria (hives). It is known for its rapid onset of action, typically within one hour of ingestion.
- Dosage: The standard adult dose is 10 mg once daily, which can be adjusted based on individual needs.
- Side Effects: While cetirizine is less sedating than diphenhydramine, it can still cause drowsiness in some individuals. Other side effects may include dry mouth, fatigue, and headache.
- Effectiveness: Studies have shown that cetirizine is effective in reducing symptoms of allergic rhinitis, with a success rate of approximately 70% in clinical trials.
Diphenhydramine: The Classic Antihistamine
Diphenhydramine, widely recognized by its brand name Benadryl, is a first-generation antihistamine that has been used for decades. It is effective for treating allergic reactions, motion sickness, and as a sleep aid due to its sedative properties.
- Dosage: The typical adult dose is 25-50 mg every 4-6 hours, not exceeding 300 mg per day.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, and urinary retention. Its sedative effects can be beneficial for those seeking relief from insomnia.
- Effectiveness: Diphenhydramine is highly effective for acute allergic reactions, with a rapid onset of action, often within 15-30 minutes.
Comparative Analysis: Cetirizine vs. Diphenhydramine
When comparing cetirizine and diphenhydramine, several factors come into play:
- Onset of Action: Diphenhydramine acts faster than cetirizine, making it suitable for immediate relief.
- Duration of Action: Cetirizine has a longer duration of action, providing relief for up to 24 hours.
- Side Effects: Cetirizine is generally better tolerated with fewer sedative effects, making it a preferred choice for daytime use.
- Use Cases: Diphenhydramine is often recommended for acute allergic reactions or as a sleep aid, while cetirizine is better suited for chronic allergy management.
Conclusion: Which is Better?
Choosing between cetirizine and diphenhydramine ultimately depends on individual needs and circumstances. If you require quick relief from acute allergy symptoms or need help sleeping, diphenhydramine may be the better option. However, for long-term management of allergies with minimal sedation, cetirizine is likely the superior choice.
Before starting any medication, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best option for your specific situation. For more information on antihistamines and their uses, you can visit the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
In summary, both cetirizine and diphenhydramine have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences can empower you to make an informed decision about your allergy management strategy.