-
Table of Contents
Zero Tax US States: A Comprehensive Guide
In the quest for financial freedom and economic opportunity, many individuals and businesses are increasingly drawn to states with no income tax. These “zero tax” states offer a unique environment that can significantly impact personal finances and business operations. This article explores the concept of zero tax states, their benefits, and the implications for residents and businesses alike.
Understanding Zero Tax States
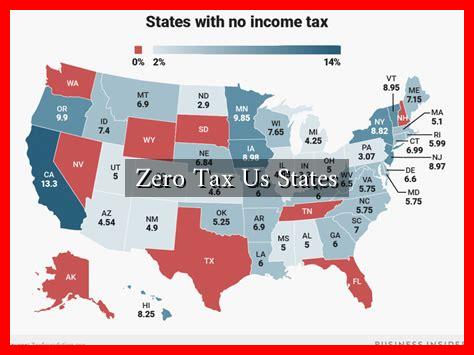
Zero tax states are those that do not impose a state income tax on individuals or corporations. This can be a significant financial advantage, especially for high earners and entrepreneurs. As of 2023, there are nine states in the U.S.
. that do not levy a personal income tax:
- Alaska
- Florida
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Washington
- Wyoming
The Benefits of Living in Zero Tax States
Choosing to reside in a zero tax state can offer numerous advantages, including:
- Increased Disposable Income: Without state income tax, residents can keep more of their earnings, leading to greater disposable income for spending, saving, or investing.
- Attractiveness for Businesses: Companies may find it more appealing to set up operations in these states, as they can save on taxes and potentially pass those savings onto consumers.
- Economic Growth: States without income tax often experience faster economic growth, attracting new residents and businesses seeking a favorable tax environment.
- Retirement Benefits: Many retirees are drawn to zero tax states, as they can enjoy their retirement savings without the burden of state income tax.
Case Studies: States with No Income Tax
Let’s take a closer look at a few notable zero tax states and how they have benefited from this tax structure:
Florida
Florida is one of the most popular zero tax states, attracting millions of residents and tourists each year. The absence of a state income tax has made it a haven for retirees and high-income earners alike. According to the Florida Department of Revenue, the state has seen a steady influx of new residents, contributing to a booming real estate market and robust tourism industry.
Texas
Texas is another prime example, known for its business-friendly environment. The lack of a state income tax has encouraged many companies, including major corporations like Tesla and Oracle, to relocate their headquarters to the Lone Star State. This has resulted in job creation and economic diversification, making Texas one of the fastest-growing states in the nation.
Washington
Washington state, while lacking a personal income tax, does impose a sales tax and various business taxes. However, its thriving tech industry, led by giants like Amazon and Microsoft, has attracted a highly skilled workforce. The state’s economy continues to flourish, demonstrating that zero income tax can coexist with other forms of taxation.
Considerations and Drawbacks
While the benefits of living in a zero tax state are appealing, there are also considerations to keep in mind:
- Higher Sales and Property Taxes: To compensate for the lack of income tax, many zero tax states impose higher sales and property taxes, which can offset some of the financial benefits.
- Limited Public Services: Some zero tax states may have fewer public services or lower funding for education and infrastructure, which can impact quality of life.
- Cost of Living Variations: The cost of living can vary significantly between zero tax states, with some areas being more expensive than others.
Conclusion
Zero tax states present a compelling option for individuals and businesses seeking to maximize their financial potential. With benefits such as increased disposable income, economic growth, and an attractive environment for businesses, these states have become increasingly popular. However, potential residents should carefully consider the trade-offs, including higher sales and property taxes and the availability of public services. Ultimately, the decision to move to a zero tax state should align with personal financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
For more information on state taxes and economic conditions, you can visit the Tax Foundation.