-
Table of Contents
Understanding the 8 Vital Signs: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to monitoring the health and well-being of individuals, healthcare professionals rely on a set of key indicators known as vital signs. These vital signs provide valuable insights into a person’s overall health status and help healthcare providers make informed decisions about their care. In this article, we will explore the 8 vital signs that are crucial for assessing a person’s health.
The 8 Vital Signs
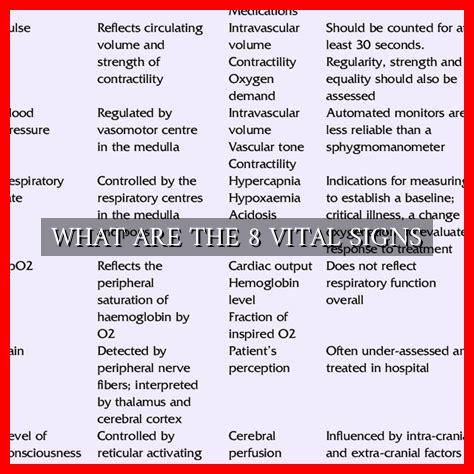
The 8 vital signs include:
- 1. Body Temperature
- 2. Heart Rate
- 3. Blood Pressure
- 4. Respiratory Rate
- 5. Oxygen Saturation
- 6. Pain Level
- 7. Blood Glucose Level
- 8. Mental Status
1. Body Temperature
Body temperature is a measure of the body’s ability to generate and get rid of heat. The normal body temperature for adults is around 98.6°F (37°C). Abnormal body temperature can indicate various health conditions, such as infection or inflammation.
2. Heart Rate
Heart rate, also known as pulse rate, is the number of times the heart beats per minute. The normal resting heart rate for adults is between 60-100 beats per minute. Changes in heart rate can be a sign of cardiovascular problems or other health issues.
3. Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of blood against the walls of the arteries. Normal blood pressure is typically around 120/80 mmHg. High blood pressure (hypertension) or low blood pressure (hypotension) can indicate underlying health problems.
4. Respiratory Rate
Respiratory rate is the number of breaths taken per minute. The normal respiratory rate for adults is 12-20 breaths per minute. Abnormal respiratory rate can be a sign of respiratory distress or other respiratory conditions.
5. Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen saturation measures the percentage of oxygen in the blood. Normal oxygen saturation levels are typically between 95-100%. Low oxygen saturation levels can indicate respiratory or cardiovascular problems.
6. Pain Level
Pain level is a subjective measure of a person’s pain intensity. Healthcare providers use various pain scales to assess and monitor pain levels in patients. Managing pain effectively is crucial for improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
7. Blood Glucose Level
Blood glucose level measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Normal blood glucose levels are typically between 70-130 mg/dL. Abnormal blood glucose levels can indicate diabetes or other metabolic disorders.
8. Mental Status
Mental status assessment evaluates a person’s cognitive function, including orientation, memory, attention, and reasoning. Changes in mental status can be a sign of neurological or psychological issues that require further evaluation and treatment.
Importance of Monitoring Vital Signs
Monitoring vital signs is essential for early detection of health problems, assessing the effectiveness of treatments, and ensuring patient safety. By regularly monitoring vital signs, healthcare providers can identify potential issues and intervene promptly to prevent complications.
For example, a sudden increase in blood pressure could indicate a hypertensive crisis requiring immediate medical attention. Similarly, a drop in oxygen saturation levels may signal respiratory distress that needs urgent intervention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the 8 vital signs is crucial for assessing a person’s health status and providing appropriate care. By monitoring these key indicators regularly, healthcare providers can identify potential problems early and take proactive measures to promote health and well-being. Remember, vital signs are not just numbers—they are valuable clues that can help save lives.
For more information on vital signs and their significance, visit CDC Vital Signs.