-
Table of Contents
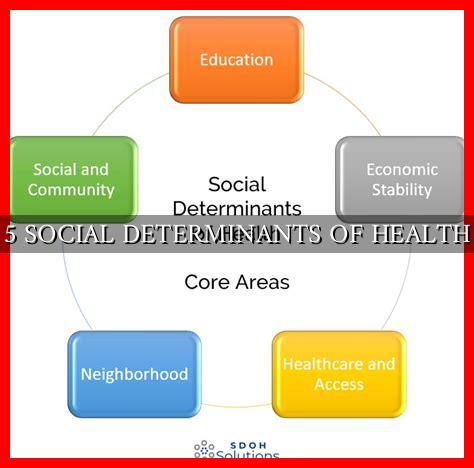
5 Social Determinants of Health
Health is influenced by a myriad of factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and access to healthcare. However, one of the most significant determinants of health is the social environment in which individuals live. Social determinants of health are the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age that impact their health outcomes. In this article, we will explore five key social determinants of health and their implications for individuals and communities.
1. Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a critical social determinant of health that encompasses factors such as income, education, and occupation. Individuals with higher SES tend to have better access to healthcare, healthier living conditions, and greater opportunities for education and employment. Conversely, those with lower SES are more likely to experience poverty, limited access to healthcare, and higher rates of chronic diseases.
- Low-income individuals are more likely to experience food insecurity, which can lead to malnutrition and obesity.
- Higher levels of education are associated with better health outcomes and lower rates of chronic diseases.
Addressing socioeconomic disparities is essential for improving overall health outcomes and reducing health inequities in society.
2. Education
Education is a powerful social determinant of health that influences individuals’ knowledge, behaviors, and access to resources. Higher levels of education are associated with better health literacy, healthier lifestyle choices, and increased opportunities for employment and economic stability.
- Individuals with lower levels of education are more likely to engage in risky behaviors such as smoking and substance abuse.
- Education can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Investing in education and promoting lifelong learning can have a significant impact on improving health outcomes and reducing health disparities.
3. Social Support Networks
Social support networks play a crucial role in promoting health and well-being. Strong social connections can provide emotional support, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging that can buffer against stress and improve mental health.
- Individuals with strong social support networks are less likely to experience depression and anxiety.
- Isolation and loneliness can have negative impacts on physical and mental health.
Building and maintaining social relationships is essential for fostering resilience and promoting overall health and well-being.
4. Physical Environment
The physical environment in which individuals live, work, and play can have a significant impact on their health outcomes. Factors such as air quality, access to green spaces, and neighborhood safety can influence individuals’ risk of chronic diseases and mental health disorders.
- Individuals living in areas with poor air quality are at higher risk of respiratory diseases such as asthma.
- Access to safe and walkable neighborhoods can promote physical activity and reduce the risk of obesity and cardiovascular diseases.
Creating healthy and sustainable environments is essential for promoting population health and reducing the burden of preventable diseases.
5. Healthcare Access
Access to healthcare is a critical social determinant of health that can significantly impact individuals’ ability to prevent, diagnose, and treat health conditions. Barriers to healthcare access, such as lack of insurance, transportation, and language barriers, can prevent individuals from receiving timely and appropriate care.
- Individuals without health insurance are less likely to receive preventive care and screenings.
- Racial and ethnic minorities are more likely to experience disparities in healthcare access and quality of care.
Improving healthcare access and addressing disparities in healthcare delivery are essential for ensuring that all individuals have the opportunity to achieve optimal health outcomes.
Conclusion
Social determinants of health play a crucial role in shaping individuals’ health outcomes and overall well-being. Addressing socioeconomic disparities, promoting education, building social support networks, creating healthy physical environments, and improving healthcare access are essential steps in reducing health inequities and promoting health equity for all individuals and communities. By recognizing and addressing these social determinants of health, we can work towards creating a healthier and more equitable society for all.