-
Table of Contents
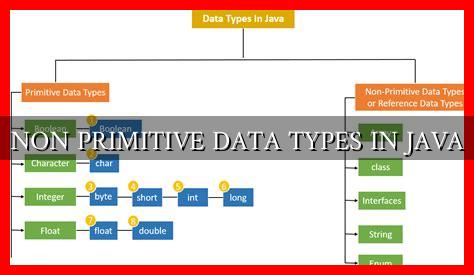
Non-Primitive Data Types in Java
When it comes to programming in Java, understanding data types is crucial. While primitive data types like int, double, and char are commonly used, non-primitive data types play a significant role in Java programming as well. In this article, we will explore non-primitive data types in Java, their characteristics, and how they differ from primitive data types.
What are Non-Primitive Data Types?
Non-primitive data types, also known as reference types, are data types that are not predefined in Java. Unlike primitive data types that store simple values, non-primitive data types store references to objects. These objects can be instances of classes, arrays, or interfaces.
Examples of Non-Primitive Data Types
Some common examples of non-primitive data types in Java include:
- String
- Arrays
- Classes
- Interfaces
Characteristics of Non-Primitive Data Types
Non-primitive data types have several key characteristics that differentiate them from primitive data types:
- Non-primitive data types are created using classes or interfaces.
- They can store complex data structures.
- Non-primitive data types are mutable, meaning their values can be changed.
- They can be null, indicating that they do not currently reference any object.
Differences Between Primitive and Non-Primitive Data Types
While primitive data types are predefined in Java and store simple values directly, non-primitive data types store references to objects.
. This distinction leads to several key differences between the two:
- Primitive data types are stored on the stack, while non-primitive data types are stored on the heap.
- Primitive data types have fixed sizes, while non-primitive data types can vary in size depending on the object they reference.
- Primitive data types are passed by value, while non-primitive data types are passed by reference.
Benefits of Using Non-Primitive Data Types
Non-primitive data types offer several advantages in Java programming:
- They allow for the creation of complex data structures.
- Non-primitive data types support object-oriented programming principles.
- They enable the creation of reusable code through classes and interfaces.
Conclusion
Non-primitive data types play a crucial role in Java programming, allowing developers to work with complex data structures and implement object-oriented programming principles. By understanding the characteristics and differences between primitive and non-primitive data types, programmers can leverage the full power of Java’s data types to create efficient and scalable applications.
For more information on non-primitive data types in Java, you can refer to the official Java documentation.