-
Table of Contents
Understanding Data Types in Java
Java is a versatile and widely-used programming language that is known for its simplicity and flexibility. One of the key features of Java is its strong typing system, which allows developers to define and manipulate different types of data. In this article, we will explore the various data types in Java and how they are used in programming.
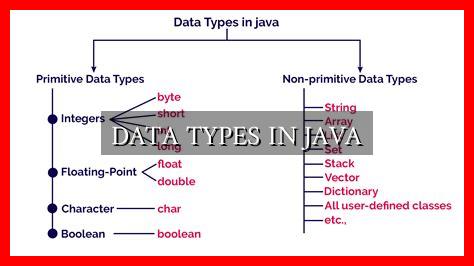
Primitive Data Types
Java has eight primitive data types that represent simple values such as integers, floating-point numbers, characters, and booleans. These data types are:
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- float
- double
- char
- boolean
Each primitive data type has a specific range of values that it can store. For example, the int data type can store integer values ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647.
Reference Data Types
In addition to primitive data types, Java also has reference data types that are used to store references to objects.
. These data types include:
- String
- Array
- Class
- Interface
Reference data types are used to store complex data structures and objects in Java programs. For example, the String data type is used to store sequences of characters.
Declaring Variables
In Java, variables must be declared with a specific data type before they can be used. The syntax for declaring a variable is:
“`java
;
“`
For example, to declare an integer variable named num, you would write:
“`java
int num;
“`
Variables can also be initialized at the time of declaration. For example:
“`java
int num = 10;
“`
Using Data Types in Java
Data types in Java are used to define the type of data that a variable can store and the operations that can be performed on that data. For example, arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division can be performed on numeric data types like int and double.
Java also provides type conversion mechanisms to convert data from one type to another. For example, you can convert an int to a double using explicit casting:
“`java
int num = 10;
double doubleNum = (double) num;
“`
Conclusion
In conclusion, data types are an essential concept in Java programming that allow developers to define and manipulate different types of data. By understanding the various data types in Java and how they are used, developers can write more efficient and reliable code. Whether you are working with primitive data types or reference data types, it is important to choose the right data type for the task at hand to ensure the success of your Java programs.
For more information on data types in Java, you can refer to the official Java documentation.