-
Table of Contents
Solutions for 8 Queens Problem
The 8 Queens Problem is a classic chess puzzle that involves placing eight queens on an 8×8 chessboard in such a way that no two queens threaten each other. This means that no two queens can be in the same row, column, or diagonal. The problem was first proposed in the mid-19th century and has since become a popular challenge in the field of computer science and mathematics.
Brute Force Approach
One of the simplest ways to solve the 8 Queens Problem is through a brute force approach. This involves generating all possible configurations of queens on the chessboard and checking each one to see if it satisfies the constraints. While this method is straightforward, it can be computationally expensive, especially for larger chessboards.
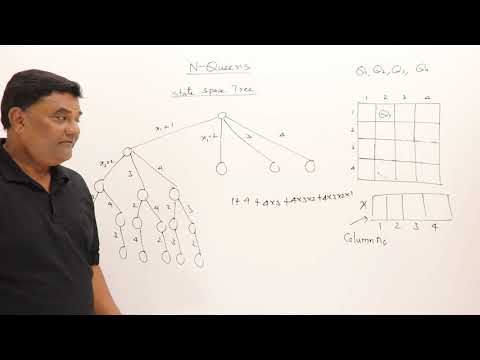
Backtracking Algorithm
A more efficient solution to the 8 Queens Problem is the backtracking algorithm.
. This algorithm works by recursively placing queens on the chessboard and backtracking when a conflict is encountered. By systematically exploring all possible configurations, the algorithm can find a valid solution without having to check every single one.
Example:
Let’s consider an example of how the backtracking algorithm can be used to solve the 8 Queens Problem:
- Start with an empty chessboard.
- Place a queen in the first row and column.
- Move to the next row and place a queen in a safe position.
- Continue this process until all queens are placed.
- If a conflict is encountered, backtrack and try a different position.
Optimizations
There are several optimizations that can be made to improve the efficiency of the backtracking algorithm for the 8 Queens Problem:
- Use symmetry to reduce the number of configurations to check.
- Prune branches that lead to conflicts early in the search.
- Implement constraint propagation techniques to eliminate invalid choices.
Case Study: N-Queens Problem
The N-Queens Problem is a generalization of the 8 Queens Problem, where the goal is to place N queens on an NxN chessboard. Researchers have developed various algorithms and heuristics to solve this problem efficiently, including genetic algorithms, simulated annealing, and constraint satisfaction techniques.
Statistics:
According to a study published in the Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, the average time complexity of solving the N-Queens Problem using backtracking is O(N!), where N is the size of the chessboard. However, with optimizations and heuristics, this complexity can be significantly reduced.
Conclusion
The 8 Queens Problem is a challenging puzzle that has inspired researchers to develop innovative solutions using algorithms and heuristics. By leveraging techniques such as backtracking and constraint propagation, it is possible to find efficient solutions to this classic problem. As technology continues to advance, new approaches and optimizations will likely emerge to tackle even larger instances of the N-Queens Problem.