-
Table of Contents
3D PRINTER: HOW DOES IT WORK
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that has transformed various industries by allowing the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital files. This process involves building objects layer by layer, unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of how 3D printers work and explore the key components that make this technology possible.
Understanding the Basics of 3D Printing
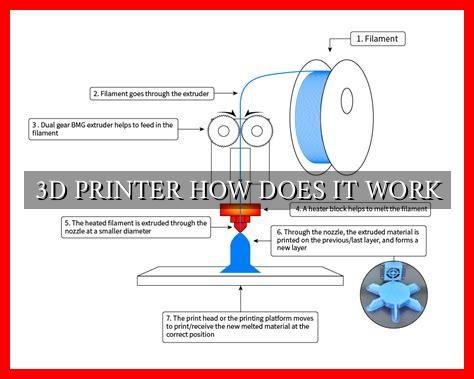
At its core, 3D printing involves the following key steps:
- Creating a 3D model: The first step in the 3D printing process is to create a digital design of the object you want to print. This can be done using computer-aided design (CAD) software or by downloading existing designs from online repositories.
- Slicing the model: Once the 3D model is ready, it needs to be sliced into thin layers using slicing software. This software generates a set of instructions that guide the 3D printer on how to build each layer of the object.
- Printing the object: The sliced layers are then sent to the 3D printer, which uses various materials such as plastic, metal, or resin to build the object layer by layer.
. The printer follows the instructions provided by the slicing software to create the final 3D object.
The Components of a 3D Printer
A typical 3D printer consists of several key components that work together to bring your digital designs to life:
- Extruder: The extruder is responsible for melting and depositing the printing material onto the build platform. It moves back and forth to create each layer of the object.
- Build platform: This is the surface on which the object is built. It moves up and down or side to side to accommodate each layer of the object as it is being printed.
- Control board: The control board acts as the brain of the 3D printer, interpreting the instructions from the slicing software and coordinating the movements of the extruder and build platform.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, each with its own unique process and materials:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM is one of the most common 3D printing technologies, where a thermoplastic filament is melted and extruded through a nozzle to create layers of the object.
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA uses a liquid resin that is cured by a UV laser to create each layer of the object. This technology is known for its high level of detail and accuracy.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses a laser to sinter powdered material, such as nylon or metal, to create each layer of the object. This technology is often used for producing functional prototypes and end-use parts.
Benefits of 3D Printing
3D printing offers numerous benefits, including:
- Rapid prototyping: 3D printing allows for the quick and cost-effective production of prototypes, enabling companies to iterate on designs faster.
- Customization: 3D printing enables the creation of highly customized products tailored to individual needs and preferences.
- Reduced waste: Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing only uses the materials needed to create the object, minimizing waste.
Conclusion
3D printing has revolutionized the way we design and manufacture objects, offering endless possibilities for innovation and creativity. By understanding how 3D printers work and the key components involved, we can appreciate the power of this technology to transform industries and drive progress. As 3D printing continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly shape the future of manufacturing and design.