-
Table of Contents
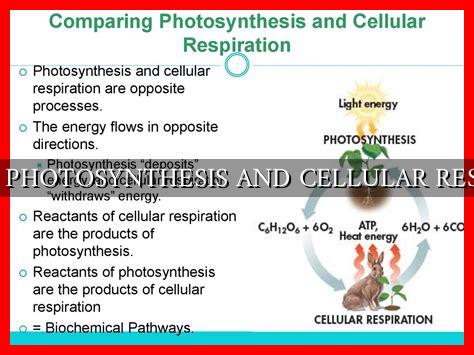
Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental processes that occur in living organisms, playing crucial roles in the energy flow within ecosystems. While they are interconnected in many ways, they also have distinct differences that set them apart. In this article, we will explore the similarities and differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, highlighting their importance in sustaining life on Earth.
Photosynthesis: The Process of Energy Production in Plants
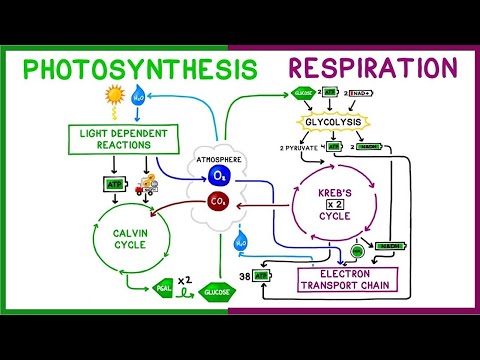
Photosynthesis is a biological process that occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria, where light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves several key steps:
- Light Absorption: Chlorophyll, a pigment found in chloroplasts, absorbs sunlight.
- Water Splitting: Water molecules are split into oxygen, protons, and electrons.
- Carbon Fixation: Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is converted into glucose through the Calvin cycle.
Photosynthesis is essential for the production of oxygen, which is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct of the process. It also serves as the primary source of energy for plants, allowing them to grow and thrive.
Cellular Respiration: The Process of Energy Release in Cells
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose to release energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
. This process occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and involves three main stages:
- Glycolysis: Glucose is broken down into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
- Krebs Cycle: Pyruvate is further broken down to release more ATP and carbon dioxide.
- Electron Transport Chain: Electrons from the Krebs cycle are used to generate a large amount of ATP.
Cellular respiration is essential for the survival of all living organisms, as it provides the energy needed for various cellular processes, such as growth, repair, and reproduction.
Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
While photosynthesis and cellular respiration are distinct processes, they are interconnected in several ways:
- Both processes involve the exchange of gases: Photosynthesis takes in carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, while cellular respiration takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
- Both processes involve the production of ATP: Photosynthesis produces ATP through the light-dependent reactions, while cellular respiration produces ATP through the electron transport chain.
- Both processes are essential for the survival of living organisms: Photosynthesis provides oxygen and glucose for plants, while cellular respiration releases energy for cellular functions.
Despite their similarities, photosynthesis and cellular respiration also have key differences:
- Photosynthesis is an anabolic process that builds complex molecules, while cellular respiration is a catabolic process that breaks down molecules.
- Photosynthesis requires light energy to drive the process, while cellular respiration does not rely on light and can occur in the absence of sunlight.
- Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, while cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two essential processes that work together to sustain life on Earth. While photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy, cellular respiration releases that energy for cellular functions. Understanding the similarities and differences between these processes is crucial for appreciating the intricate balance of energy flow within ecosystems.
For further reading on the topic, you can explore this Khan Academy article on photosynthesis in plants.