-
Table of Contents
How Does Climate Change Influence the Timing of Fall Harvests?
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, affecting various aspects of life, including agriculture. As global temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, the timing of fall harvests is increasingly impacted. This article explores how climate change influences the timing of these harvests, the implications for farmers, and the broader effects on food security.
The Science Behind Climate Change and Agriculture
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions. These changes can significantly affect agricultural practices, particularly the timing of planting and harvesting crops. Key factors include:
- Temperature Increases: Warmer temperatures can accelerate crop growth, leading to earlier harvests.
- Altered Precipitation Patterns: Changes in rainfall can affect soil moisture levels, impacting crop yields and harvest timing.
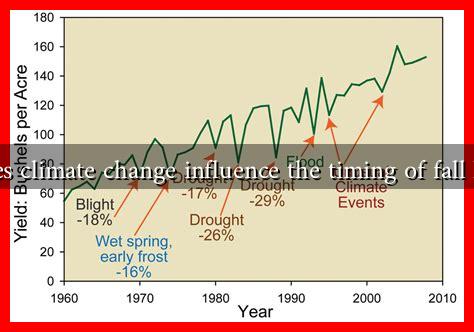
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased frequency of droughts, floods, and storms can disrupt traditional farming schedules.
Shifting Harvest Dates: A Closer Look
Research indicates that many regions are experiencing shifts in the timing of fall harvests. For instance, a study published in the journal Global Change Biology found that in the United States, the harvest of corn and soybeans has advanced by an average of 1.5 days per decade since the 1980s. This shift can be attributed to rising temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns.
Case Studies: Regional Impacts
Different regions are experiencing unique challenges and changes due to climate change:
- Midwestern United States: Farmers in states like Iowa and Illinois are noticing that corn is maturing faster, leading to earlier harvests. This can be beneficial in some years but poses risks if early frosts occur.
- California: The state’s agricultural sector is facing challenges due to prolonged droughts and water shortages, which can delay planting and subsequently affect harvest timing.
- Europe: In countries like France and Germany, grape harvests for wine production are occurring earlier, impacting the quality and characteristics of the wine produced.
Implications for Farmers and Food Security
The shifting timing of fall harvests has significant implications for farmers and food security:
- Crop Management: Farmers must adapt their planting schedules and crop management practices to align with changing climate conditions.
- Pest and Disease Pressure: Warmer temperatures can lead to increased pest populations and disease outbreaks, complicating harvests.
- Market Dynamics: Early or late harvests can affect market prices, leading to economic uncertainty for farmers.
Adapting to Change: Strategies for Farmers
To mitigate the impacts of climate change on harvest timing, farmers can adopt several strategies:
- Crop Diversification: Growing a variety of crops can reduce risk and improve resilience against climate variability.
- Improved Irrigation Techniques: Efficient water management can help mitigate the effects of drought and ensure optimal growing conditions.
- Utilizing Technology: Precision agriculture tools can help farmers monitor weather patterns and soil conditions, allowing for better planning and decision-making.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Climate change is undeniably reshaping the agricultural landscape, particularly the timing of fall harvests. As temperatures rise and weather patterns become more unpredictable, farmers must adapt to these changes to ensure food security and economic stability. By embracing innovative practices and technologies, the agricultural sector can navigate the challenges posed by climate change, ultimately contributing to a more resilient food system.
In summary, understanding the influence of climate change on fall harvests is crucial for farmers, policymakers, and consumers alike. As we move forward, collaboration and proactive measures will be essential in addressing the challenges posed by a changing climate.