-
Table of Contents
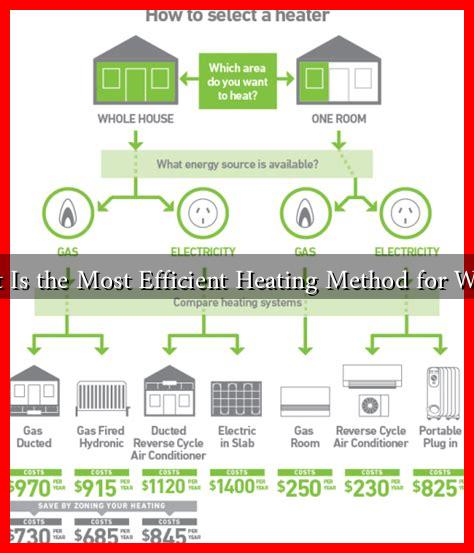
What Is the Most Efficient Heating Method for Winter?
As winter approaches, the quest for an efficient heating method becomes paramount for homeowners and renters alike. With rising energy costs and environmental concerns, selecting the right heating system can significantly impact both your wallet and the planet. This article explores various heating methods, their efficiency, and how to choose the best option for your needs.
Understanding Heating Efficiency
Heating efficiency is typically measured by the amount of heat produced per unit of energy consumed. The higher the efficiency rating, the less energy is wasted. Common metrics include:
- Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE): This measures the efficiency of furnaces and boilers.
- Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER): This is used for air conditioning systems but can also apply to heat pumps.
- Coefficient of Performance (COP): This measures the efficiency of heat pumps, indicating how much heat is produced for each unit of electricity consumed.
Popular Heating Methods
Several heating methods are commonly used in homes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a breakdown of the most popular options:
1. Central Heating Systems
Central heating systems, such as furnaces and boilers, are widely used in residential settings. They distribute heat through ducts or pipes, providing consistent warmth throughout the home.
- Furnaces: Typically powered by natural gas, oil, or electricity, modern furnaces can achieve AFUE ratings of over 90%.
- Boilers: These systems heat water and distribute steam or hot water through radiators. High-efficiency models can also exceed 90% AFUE.
2. Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficiency and versatility. They can both heat and cool a home, making them a year-round solution.
- Air-source heat pumps: These extract heat from the outside air, even in cold temperatures. They can achieve SEER ratings of 15 or higher.
- Ground-source (geothermal) heat pumps: These systems use the earth’s stable temperature to provide heating and cooling, boasting COP ratings often above 4.0.
3. Electric Heating
Electric heating systems, such as baseboard heaters and electric furnaces, are easy to install and maintain. However, they can be less efficient in terms of energy costs, especially in areas where electricity prices are high.
- Baseboard heaters: These provide localized heating but can lead to higher energy bills if used extensively.
- Electric furnaces: While they can be efficient, their operating costs can be prohibitive in colder climates.
Case Studies and Statistics
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can be 300% to 400% efficient, meaning they produce three to four times more energy in heat than they consume in electricity. A case study in a New York home showed that switching from a traditional furnace to a geothermal heat pump reduced heating costs by 50% annually.
Furthermore, a report from the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE) indicates that homes using high-efficiency furnaces and heat pumps can save up to $1,000 per year compared to those using older, less efficient systems.
Choosing the Right Heating Method
When selecting the most efficient heating method for your home, consider the following factors:
- Climate: Colder climates may benefit more from heat pumps or high-efficiency furnaces.
- Home Size: Larger homes may require central heating systems, while smaller spaces might be adequately heated with electric options.
- Energy Costs: Analyze local energy prices to determine the most cost-effective heating method.
- Environmental Impact: Consider renewable energy options, such as geothermal heat pumps, to reduce your carbon footprint.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the most efficient heating method for winter largely depends on individual circumstances, including climate, home size, and energy costs. Heat pumps, particularly geothermal systems, stand out for their high efficiency and dual functionality. However, high-efficiency furnaces and boilers also offer significant savings and comfort. By carefully evaluating your options and considering both economic and environmental factors, you can make an informed decision that keeps your home warm while minimizing costs and impact on the planet.
For more information on energy-efficient heating solutions, visit the U.S. Department of Energy’s website.