-
Table of Contents
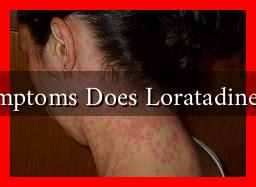
What Symptoms Does Loratadine Relieve?
Loratadine is a widely used antihistamine that is primarily known for its effectiveness in alleviating allergy symptoms. As a second-generation antihistamine, it is favored for its non-drowsy properties, making it a popular choice for individuals seeking relief from various allergic reactions without the sedative effects associated with first-generation antihistamines. This article delves into the specific symptoms that loratadine can relieve, its mechanism of action, and relevant considerations for its use.
Understanding Loratadine
Loratadine, marketed under brand names such as Claritin and Alavert, is an antihistamine that works by blocking the action of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic symptoms. It is commonly available over-the-counter and is used to treat a variety of conditions related to allergies.
Common Symptoms Relieved by Loratadine
Loratadine is effective in relieving a range of symptoms associated with allergic reactions and other conditions. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Runny or Stuffy Nose: Loratadine helps reduce nasal congestion and runny nose, which are common symptoms of allergic rhinitis.
- Itchy or Watery Eyes: The medication alleviates eye discomfort caused by allergies, providing relief from itching and excessive tearing.
- Sneezing: Loratadine can help reduce the frequency and intensity of sneezing episodes triggered by allergens.
- Itchy Throat or Nose: The antihistamine effect of loratadine can soothe irritation in the throat and nasal passages.
- Skin Reactions: Loratadine is also effective in managing symptoms of allergic skin reactions, such as hives and itching.
Mechanism of Action
The effectiveness of loratadine in relieving allergy symptoms can be attributed to its mechanism of action. As a selective antagonist of peripheral H1 receptors, loratadine blocks the effects of histamine, which is released during allergic reactions. By inhibiting histamine’s action, loratadine reduces the symptoms associated with allergies without crossing the blood-brain barrier, which minimizes sedation.
Case Studies and Statistics
Research has shown that loratadine is effective in managing allergy symptoms. A study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that loratadine significantly improved symptoms of allergic rhinitis compared to a placebo. In this study, participants reported a 50% reduction in sneezing and nasal congestion after taking loratadine for just one week.
Furthermore, a survey conducted by the American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology (ACAAI) indicated that approximately 30% of adults in the United States suffer from allergic rhinitis, with many relying on antihistamines like loratadine for relief. This statistic underscores the importance of effective allergy management in improving quality of life.
Considerations and Side Effects
While loratadine is generally well-tolerated, it is essential to consider potential side effects. Some individuals may experience:
- Headache
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Gastrointestinal disturbances
It is advisable for individuals with certain medical conditions or those taking other medications to consult a healthcare provider before using loratadine. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also seek medical advice to ensure safety.
Conclusion
Loratadine is a highly effective antihistamine that provides relief from a variety of allergy-related symptoms, including nasal congestion, sneezing, and itchy eyes. Its non-drowsy formulation makes it a preferred choice for many individuals seeking to manage their allergies without the sedative effects of older antihistamines. With a solid understanding of its benefits, mechanism of action, and potential side effects, users can make informed decisions about incorporating loratadine into their allergy management plan. As always, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to ensure the best outcomes for individual health needs.