-
Table of Contents
How Does Insulin Impact Blood Sugar Levels?
Insulin is a vital hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. Understanding how insulin functions can provide valuable insights into managing conditions like diabetes and maintaining overall health. This article delves into the mechanisms of insulin, its impact on blood sugar levels, and the implications for individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes.
The Role of Insulin in the Body
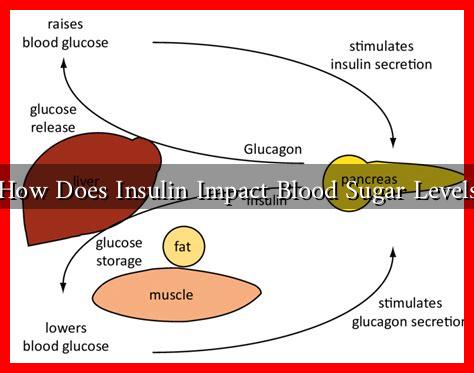
Insulin is primarily responsible for controlling glucose levels in the bloodstream. When we consume food, particularly carbohydrates, our body breaks it down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. The pancreas responds to rising blood sugar levels by releasing insulin. This hormone facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use.
How Insulin Lowers Blood Sugar Levels
Insulin lowers blood sugar levels through several mechanisms:
- Facilitating Glucose Uptake: Insulin binds to receptors on cell surfaces, allowing glucose to enter cells, particularly in muscle and fat tissues.
- Promoting Glycogen Storage: In the liver and muscles, insulin encourages the conversion of excess glucose into glycogen, a stored form of glucose.
- Inhibiting Gluconeogenesis: Insulin suppresses the liver’s production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, further reducing blood sugar levels.
These actions collectively help maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range, typically between 70 and 130 mg/dL before meals, according to the American Diabetes Association.
Insulin Resistance and Its Effects
In some individuals, particularly those with obesity or metabolic syndrome, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin. This condition, known as insulin resistance, means that more insulin is required to achieve the same effect on blood sugar levels. As a result, the pancreas compensates by producing more insulin, which can lead to several health issues:
- Increased Blood Sugar Levels: Over time, insulin resistance can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Gain: High insulin levels can promote fat storage, contributing to obesity.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Insulin resistance is associated with higher risks of heart disease and stroke.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 34 million Americans have diabetes, with a significant portion of these cases linked to insulin resistance.
Case Study: The Impact of Insulin on Blood Sugar Management
A study published in the journal Diabetes Care examined the effects of insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. The researchers found that those who received insulin therapy experienced a significant reduction in HbA1c levels, a marker of long-term blood sugar control, compared to those who did not. This highlights the importance of insulin in managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Conclusion: The Importance of Insulin in Blood Sugar Regulation
Insulin is a critical hormone that plays a fundamental role in regulating blood sugar levels. By facilitating glucose uptake, promoting glycogen storage, and inhibiting glucose production, insulin helps maintain homeostasis in the body. However, conditions like insulin resistance can disrupt this balance, leading to serious health consequences.
Understanding the impact of insulin on blood sugar levels is essential for individuals managing diabetes or those at risk of developing metabolic disorders. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, individuals can improve their insulin sensitivity and overall health.
In summary, insulin is not just a hormone; it is a key player in the intricate dance of blood sugar regulation. Awareness and management of insulin levels can lead to better health outcomes and a higher quality of life.