-
Table of Contents
- Is it Possible to Have a Resistance to Azithromycin?
- Understanding Azithromycin and Its Mechanism of Action
- The Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance
- Mechanisms of Resistance to Azithromycin
- Prevalence of Azithromycin Resistance
- Case Studies Highlighting Resistance
- Implications for Treatment
- Conclusion
Is it Possible to Have a Resistance to Azithromycin?
Azithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, is widely used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. However, the emergence of antibiotic resistance poses a significant challenge to public health. This article explores the possibility of resistance to azithromycin, the mechanisms behind it, and its implications for treatment.
Understanding Azithromycin and Its Mechanism of Action
Azithromycin works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, effectively stopping the growth of bacteria. It is particularly effective against Gram-positive bacteria and some Gram-negative bacteria. The drug is often prescribed due to its favorable pharmacokinetics, including a long half-life and the ability to penetrate tissues effectively.
The Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve mechanisms to resist the effects of drugs that once killed them or inhibited their growth. This phenomenon is a growing concern in the medical community, as it can lead to treatment failures and increased morbidity and mortality rates.
Mechanisms of Resistance to Azithromycin
Resistance to azithromycin can occur through several mechanisms:
- Target Modification: Bacteria can alter the ribosomal RNA (rRNA) that azithromycin targets, reducing the drug’s binding affinity.
- Efflux Pumps: Some bacteria possess efflux pumps that actively expel azithromycin from their cells, decreasing its intracellular concentration.
- Enzymatic Inactivation: Certain bacteria can produce enzymes that modify or degrade azithromycin, rendering it ineffective.
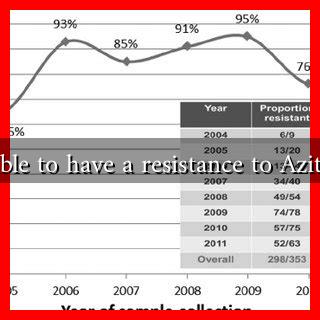
Prevalence of Azithromycin Resistance
Research indicates that azithromycin resistance is on the rise globally. A study published in the journal Clinical Microbiology Reviews reported that resistance rates can vary significantly by region and bacterial species. For instance:
- In the United States, resistance rates among Streptococcus pneumoniae have been reported to be as high as 30%.
- In some parts of Asia, resistance rates in Neisseria gonorrhoeae have reached alarming levels, prompting concerns about treatment failures.
Case Studies Highlighting Resistance
Several case studies illustrate the impact of azithromycin resistance:
- A 2019 case in the UK involved a patient with a severe respiratory infection caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which was resistant to azithromycin, leading to prolonged hospitalization and the need for alternative treatments.
- In 2020, a study in South Africa found that azithromycin resistance in Chlamydia trachomatis was associated with treatment failures, highlighting the need for susceptibility testing before prescribing.
Implications for Treatment
The rise of azithromycin resistance has significant implications for clinical practice:
- Increased Treatment Failures: Patients may experience prolonged illness or complications due to ineffective treatment.
- Need for Alternative Therapies: Healthcare providers may need to resort to less effective or more toxic antibiotics, increasing the risk of side effects.
- Importance of Susceptibility Testing: Routine testing for antibiotic susceptibility can help guide appropriate therapy and reduce the risk of resistance development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, azithromycin resistance is a growing concern that poses challenges to effective treatment of bacterial infections. Understanding the mechanisms of resistance and its prevalence is crucial for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about antibiotic use. As resistance rates continue to rise, the importance of responsible antibiotic prescribing and the need for ongoing research into alternative treatments cannot be overstated. By addressing these issues, we can work towards preserving the efficacy of azithromycin and other antibiotics for future generations.