-
Table of Contents
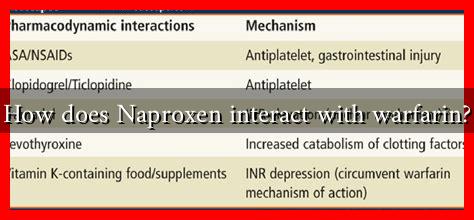
How Does Naproxen Interact with Warfarin?
Naproxen and warfarin are two commonly used medications that serve different purposes. Naproxen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) often used to relieve pain, while warfarin is an anticoagulant prescribed to prevent blood clots. Understanding the interaction between these two drugs is crucial for patients who may be prescribed both, as the combination can lead to serious health risks.
Understanding the Medications
Before delving into their interactions, it is essential to understand the mechanisms of both medications:
- Naproxen: This NSAID works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are chemicals in the body involved in inflammation, pain, and fever. It is commonly used for conditions like arthritis, menstrual pain, and other inflammatory disorders.
- Warfarin: Warfarin functions by inhibiting vitamin K epoxide reductase, an enzyme critical for the synthesis of clotting factors in the liver. It is primarily used to prevent thromboembolic events in patients with conditions such as atrial fibrillation or after certain surgeries.
The Interaction Between Naproxen and Warfarin
The interaction between naproxen and warfarin is significant and can lead to an increased risk of bleeding. This is primarily due to the following reasons:
- Increased Anticoagulant Effect: Naproxen can enhance the anticoagulant effect of warfarin, leading to a higher risk of bleeding complications. This occurs because NSAIDs can cause gastrointestinal irritation and ulceration, which may result in bleeding.
- Displacement from Protein Binding: Both naproxen and warfarin are highly protein-bound drugs. When naproxen is introduced, it can displace warfarin from its protein-binding sites, increasing the free concentration of warfarin in the bloodstream and enhancing its effects.
- Impact on Liver Metabolism: Naproxen may also affect the liver enzymes responsible for metabolizing warfarin, further complicating the anticoagulation management.
Clinical Evidence and Case Studies
Several studies have highlighted the risks associated with the concurrent use of naproxen and warfarin. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis found that patients taking NSAIDs alongside warfarin had a significantly higher incidence of major bleeding events compared to those on warfarin alone.
In a case study involving a 72-year-old patient with osteoarthritis on warfarin therapy, the addition of naproxen led to an unexpected increase in INR (International Normalized Ratio), a measure of blood coagulation. The patient’s INR rose to 5.0, indicating a high risk of bleeding, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
Monitoring and Management Strategies
Given the potential risks, it is crucial for healthcare providers to monitor patients closely when prescribing naproxen to those already on warfarin. Here are some recommended strategies:
- Regular INR Monitoring: Patients should have their INR levels checked more frequently when starting or stopping naproxen to ensure they remain within the therapeutic range.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about the signs of bleeding, such as unusual bruising, blood in urine or stool, and prolonged bleeding from cuts, is essential.
- Consider Alternatives: In some cases, healthcare providers may consider alternative pain management options that do not interact with warfarin, such as acetaminophen.
Conclusion
The interaction between naproxen and warfarin poses significant risks, primarily due to the increased likelihood of bleeding complications. Understanding these interactions is vital for both healthcare providers and patients. Regular monitoring of INR levels, patient education, and considering alternative medications can help mitigate these risks. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to medication regimens, especially when dealing with anticoagulants like warfarin.
In summary, while naproxen can be effective for pain relief, its use in patients on warfarin requires careful consideration and management to ensure patient safety.