-
Table of Contents
Understanding the Mechanics of a 2-Stroke Engine
When it comes to engines, the 2-stroke engine is a unique and efficient design that has been used in various applications, from motorcycles to chainsaws. In this article, we will delve into how a 2-stroke engine works, its advantages, and its limitations.
How Does a 2-Stroke Engine Work?
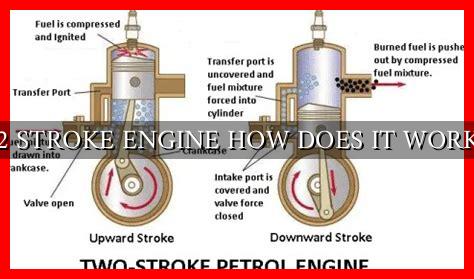
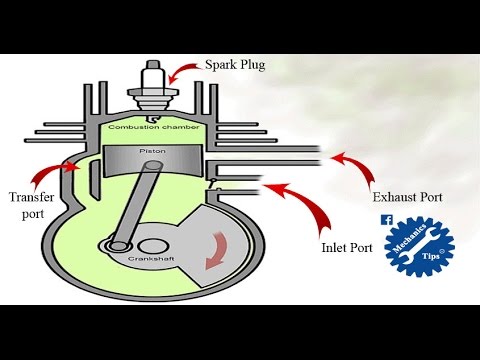
A 2-stroke engine operates on a simple principle: it completes the four necessary strokes of the piston (intake, compression, power, and exhaust) in just two movements of the piston. Let’s break down the process:
- Intake: The piston moves downward, creating a vacuum in the combustion chamber. This vacuum draws in a mixture of air and fuel through the intake port.
- Compression: As the piston moves back up, it compresses the air-fuel mixture. This compression increases the efficiency of combustion.
- Power: When the piston reaches the top of its stroke, a spark plug ignites the compressed mixture.
. This ignition creates a rapid expansion of gases, driving the piston back down with force.
- Exhaust: Finally, the piston moves back up, pushing the exhaust gases out through the exhaust port. This completes one cycle of the engine.
Advantages of 2-Stroke Engines
2-stroke engines offer several advantages over their 4-stroke counterparts:
- Simplicity: With fewer moving parts, 2-stroke engines are easier to maintain and repair.
- Power-to-weight ratio: Due to their design, 2-stroke engines are lighter and more compact, making them ideal for applications where weight is a concern.
- High power output: The rapid combustion process of a 2-stroke engine results in higher power output compared to a 4-stroke engine of similar size.
Limitations of 2-Stroke Engines
Despite their advantages, 2-stroke engines also have some limitations:
- Fuel efficiency: 2-stroke engines tend to consume more fuel than 4-stroke engines due to their design.
- Emissions: 2-stroke engines produce higher levels of emissions, including unburned hydrocarbons and particulate matter, compared to 4-stroke engines.
- Oil consumption: In a 2-stroke engine, oil must be mixed with the fuel to lubricate the moving parts, leading to higher oil consumption.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 2-stroke engine is a unique and efficient design that offers several advantages, such as simplicity and high power output. However, it also has limitations, including lower fuel efficiency and higher emissions. Understanding how a 2-stroke engine works can help you appreciate its strengths and weaknesses in various applications.
For more information on 2-stroke engines, you can visit Popular Mechanics.